JRMGE / Vol 14 / Issue 3
Improved uranium leaching efficiency from low-permeability sandstone using low-frequency vibration in the CO2+O2 leaching process
Yong Zhao, Yong Gao, Caiwu Luo, Jun Liu
Show More
a School of Resource Environment and Safety Engineering, University of South China, Hengyang, 421001, China
b Department of Nuclear Safety, China Institute of Atomic Energy, Beijing, 100000, China
c College of Humanities and Foreign Languages, Xi’an University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, 710054, China
d China Coal Technology Engineering Group Chongqing Research Institute, Chongqing 400039, China
2022, 14(3): 770-780. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.10.013
Received: 2021-03-22 / Revised: 2021-07-21 / Accepted: 2021-10-18 / Available online: 2021-12-30
2022, 14(3): 770-780.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.10.013
Received: 2021-03-22
Revised: 2021-07-21
Accepted: 2021-10-18
Available online: 2021-12-30
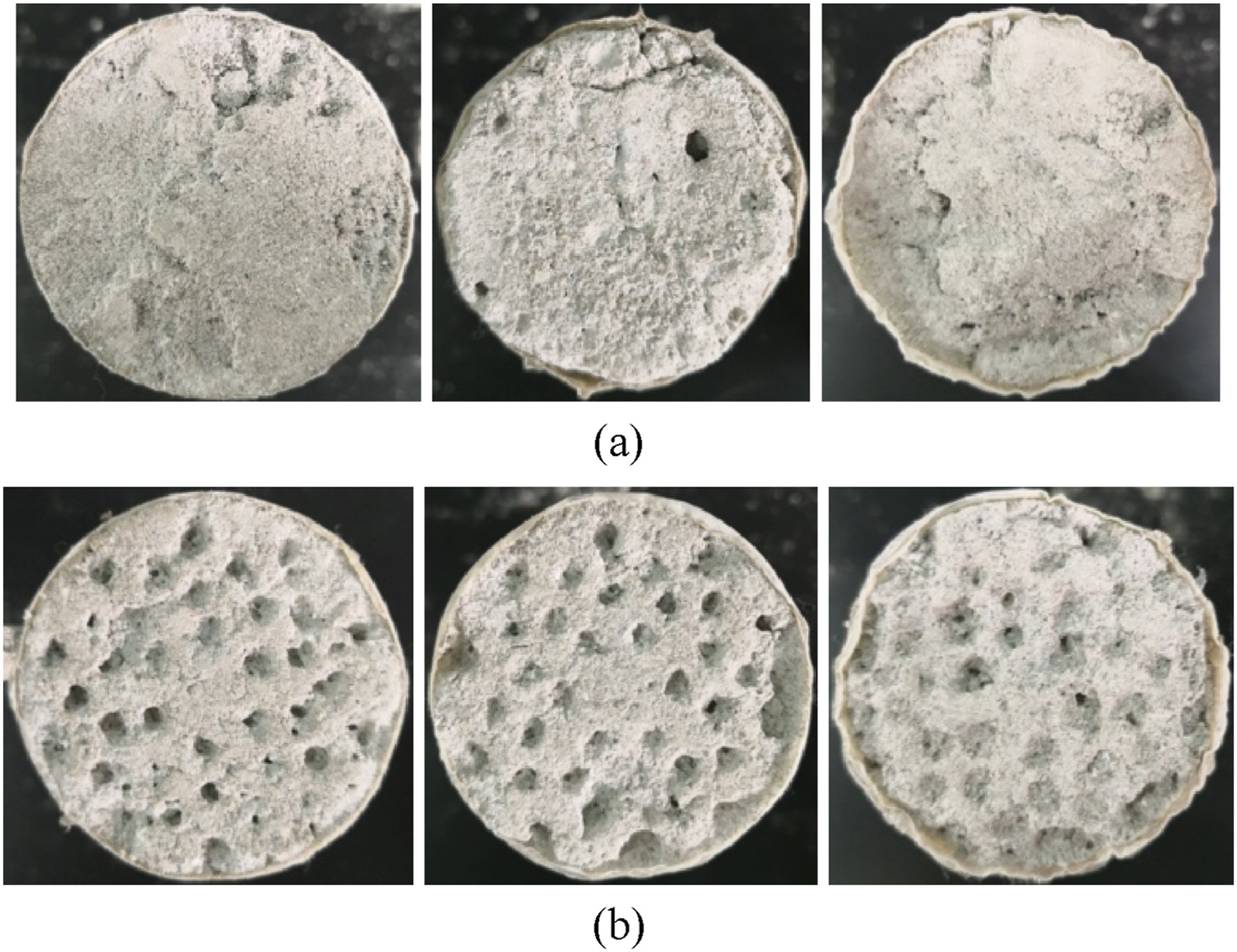
Extraction of uranium from low-permeability sandstone is a long-standing challenge in mining. The improvement of sandstone permeability has therefore become a key research focus to improve the uranium leaching effect. To address the low-permeability problem and corresponding leaching limits, leaching experiments are performed using newly developed equipment that could apply low-frequency vibration to the sandstone samples. The test results indicate that low-frequency vibration significantly improves the uranium leaching performance and permeability of the sandstone samples. The leaching effect of low-frequency vibration treatment is approximately nine times more effective than ultrasonic vibration treatment, whereas the concentration of uranium ions generated without vibration treatment is not detectable. Mathematical model that considers the combined action of physico-mechanical vibration and chemical erosion is established to describe the effect of low-frequency vibration on the permeability. The calculated results are in good agreement with the tested permeability values. This study thus offers a new method to effectively leach more uranium from low-permeability sandstone using CO2+O2 and provides an insight into the impact of low-frequency vibration on the uranium leaching process.
Keywords: Uranium leaching, Low-frequency vibration, Chemical erosion, Low permeability, Permeability model
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Yong Zhao

Yong Zhao obtained his BSc degree in Mining Engineering from Henan Polytechnic University, China, in 2008, his MSc and PhD degrees in Safety Technology and Engineering from Xi'an University of Science and Technology, China, in 2011 and 2014, respectively. He was employed by University of South China as Lecturer. Currently, he is performing the postdoctoral work at China Institute of Atomic Energy. His research interests cover laboratory testing, nuclear waste disposal, radioactive nuclide migration, constitutive modeling, environmental geotechnics, etc.