JRMGE / Vol 15 / Issue 6
Undrained vane shear strength of sand-foam mixtures subjected to different shear rates
Jiazheng Zhong, Shuying Wang, Tongming Qu
Show More
a School of Civil Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, 410075, China
b Tunnel and Underground Engineering Research Center, Central South University, Changsha, 410075, China
c Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Clearwater Bay, Hong Kong, China
2023, 15(6): 1591-1602. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.11.002
Received: 2022-06-09 / Revised: 2022-09-28 / Accepted: 2022-11-14 / Available online: 2022-11-29
2023, 15(6): 1591-1602.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.11.002
Received: 2022-06-09
Revised: 2022-09-28
Accepted: 2022-11-14
Available online: 2022-11-29
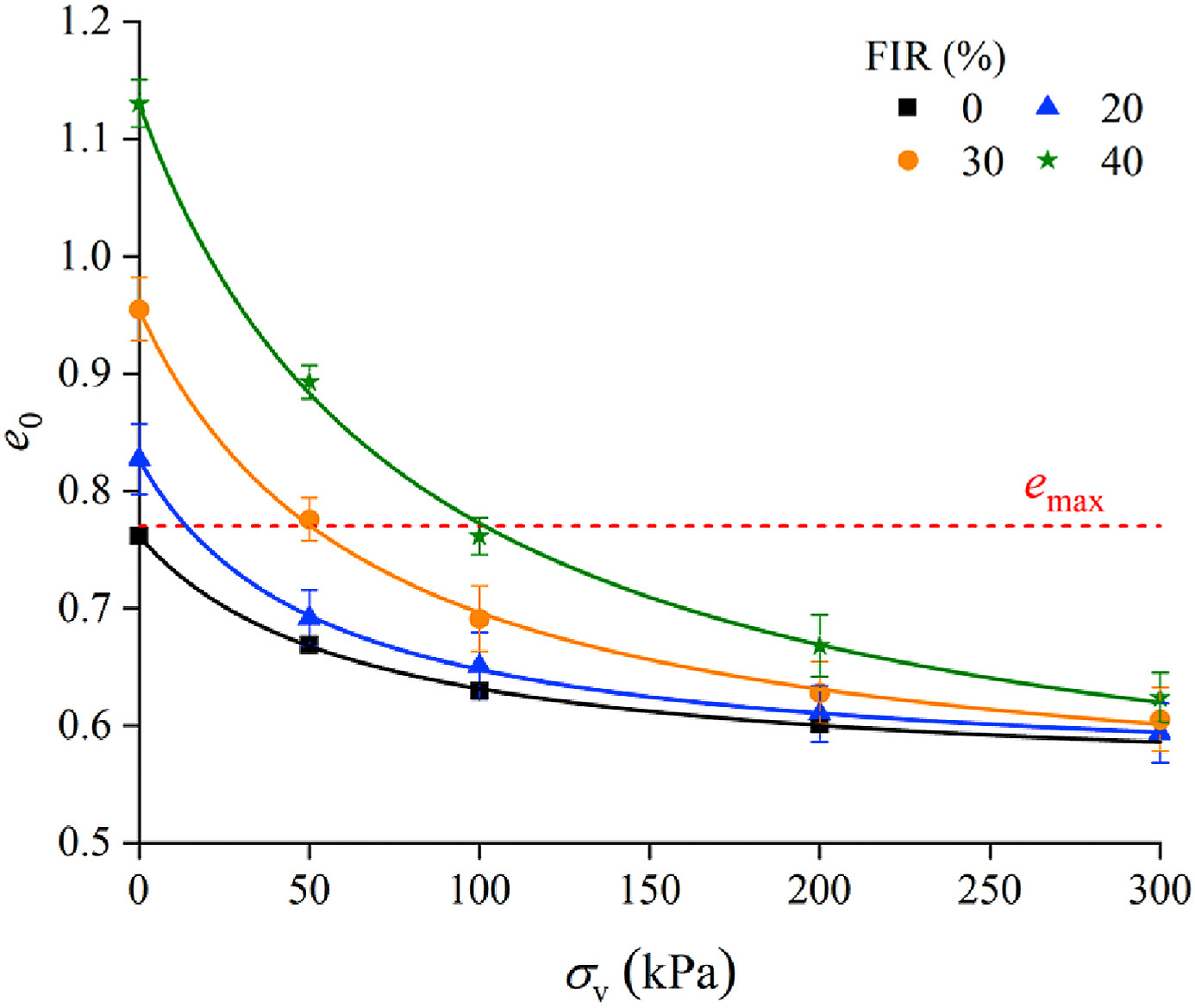
The shear strength of sand-foam mixtures plays a crucial role in ensuring successful earth pressure balance (EPB) shield tunneling. Since the sand-foam mixtures are constantly sheared by the cutterhead and the screw conveyor with varied rotation speeds during tunneling, it is non-trivial to investigate the effect of shear rates on the undrained shear strength of sand-foam mixtures under chamber pressures to extend the understanding on the tunneling process. This study conducted a series of pressurized vane shear tests to investigate the role of shear rates on the peak and residual strengths of sand-foam mixtures at different pore states. Different from the shear-rate characteristics of natural sands or clay, the results showed that the peak strength of sand-foam mixtures under high vertical total stress (σv ≥ 200 kPa) and low foam injection ratio (FIR ≤ 30%) decreased with the increase in shear rate. Otherwise, the peak strength was not measurably affected by shear rates. The sand-foam mixtures in the residual state resembled low-viscous fluid with yield stress and the residual strength increased slightly with shear rates. In addition, the peak and residual strengths were approximately linear with vertical effective stress regardless of the total stress and FIR. The peak effective internal friction angle remained almost invariant in a low shear rate (γ˙ < 0.25 s−1) but decreased when the shear rate continued increasing. The residual effective internal friction angle was lower than the peak counterpart and insensitive to shear rates. This study unveiled the role of shear rates in the undrained shear strength of sand-foam mixtures with various FIRs and vertical total stresses. The findings can extend the understanding of the rate-dependent shear characteristics of conditioned soils and guide the decision-making of soil conditioning schemes in the EPB shield tunneling practice.
Keywords: Sand-foam mixture, Shear rate, Peak and residual strengths, Effective stress, Effective internal friction angle
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Tongming Qu
✉️ tongmingqu@ust.hk

Dr. Tongming Qu is now working at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) as a post-doctoral fellow. He obtained his PhD in Civil Engineering from Swansea University (UK) in 2021, and both master and bachelor degrees from Central South University (China). His research focuses on developing novel computational (numerical and data-driven) approaches for the simulation and prediction of granular materials, with an emphasis on geotechnical and underground engineering applications. Tongming is devoted to vision-driven and problem-driven research to advance granular media-related knowledge and engineering innovations.