JRMGE / Vol 16 / Issue 2
Analysis of pressure response at an observation well against pressure build-up by early stage of CO2 geological storage project
Qiang Sun, Kyuro Sasaki, Qinxi Dong, Zhenni Ye, Hui Wang, Huan Sun
Show More
a School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, Hainan University, Haikou, 570228, China
b Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University, 744 Motooka, Nishi-ku, Fukuoka, 819-0385, Japan
c Key Laboratory of Equipment Safety and Intelligent Technology for Guangzhou Rail Transit System, Guangzhou, 510430, China
2024, 16(2): 470-482. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.013
Received: 2022-12-06 / Revised: 2023-02-14 / Accepted: 2023-03-12 / Available online: 2023-04-22
2024, 16(2): 470-482.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.013
Received: 2022-12-06
Revised: 2023-02-14
Accepted: 2023-03-12
Available online: 2023-04-22
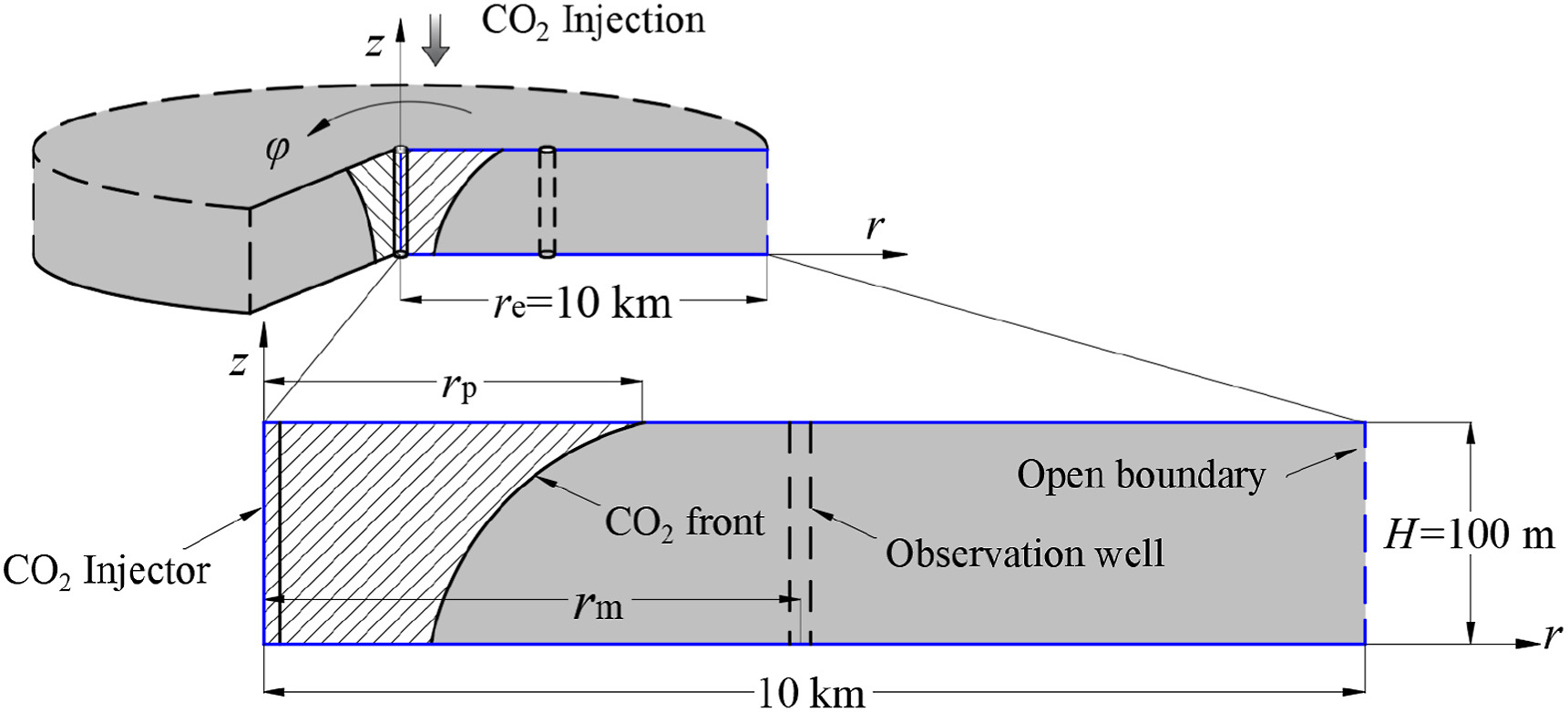
To ensure a safe and stable CO2 storage, pressure responses at an observation well are expected to be an important and useful field monitoring item to estimate the CO2 storage behaviors and the aquifer parameters during and after injecting CO2, because it can detect whether the injected CO2 leaks to the ground surface or the bottom of the sea. In this study, pressure responses were simulated to present design factors such as well location and pressure transmitter of the observation well. Numerical simulations on the pressure response and the time-delay from pressure build-up after CO2 injection were conducted by considering aquifer parameters and distance from the CO2 injection well to an observation well. The measurement resolution of a pressure transmitter installed in the observation well was presented based on numerical simulation results of the pressure response against pressure build-up at the injection well and CO2 plume front propagations. Furthermore, the pressure response at an observation well was estimated by comparing the numerical simulation results with the curve of CO2 saturation and relative permeability. It was also suggested that the analytical solution can be used for the analysis of the pressure response tendency using pressure build-up and dimensionless parameters of hydraulic diffusivity. Thus, a criterion was established for selecting a pressure transducer installed at an observation well to monitor the pressure responses with sufficient accuracy and resolution, considering the distance from the injection well and the pressure build-up at the injection well, for future carbon capture and storage (CCS) projects.
Keywords: CO2 storage, Saline aquifer, Observation well, Pressure response, CO2 saturation
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Qiang Sun

Qiang Sun obtained his BSc and MSc degrees in Shandong University of Science and Technology and China University of Mining and Technology, China, in 2013 and 2016, respectively, and his PhD in Kyushu University, Japan, in 2021. He is doing postdoctoral research at Hainan University, China since 2022. His research interests include (1) experimental investigations on the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) behaviors of host rocks for geological storage of CO2 in saline aquifer and (2) theoretical study and numerical modeling of coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) behaviors in porous media and cap rock system.