JRMGE / Vol 16 / Issue 2
Numerical analysis of geosynthetic-reinforced embankment performance under moving loads
Xuanming Ding, Jinqiao Zhao, Qiang Ou, Jianfei Liu
Show More
a College of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
b Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
c China United Engineering Corporation Limited, Hangzhou, 310052, China
2024, 16(2): 682-696. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.019
Received: 2022-11-30 / Revised: 2023-03-22 / Accepted: 2023-04-12 / Available online: 2023-07-15
2024, 16(2): 682-696.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.019
Received: 2022-11-30
Revised: 2023-03-22
Accepted: 2023-04-12
Available online: 2023-07-15
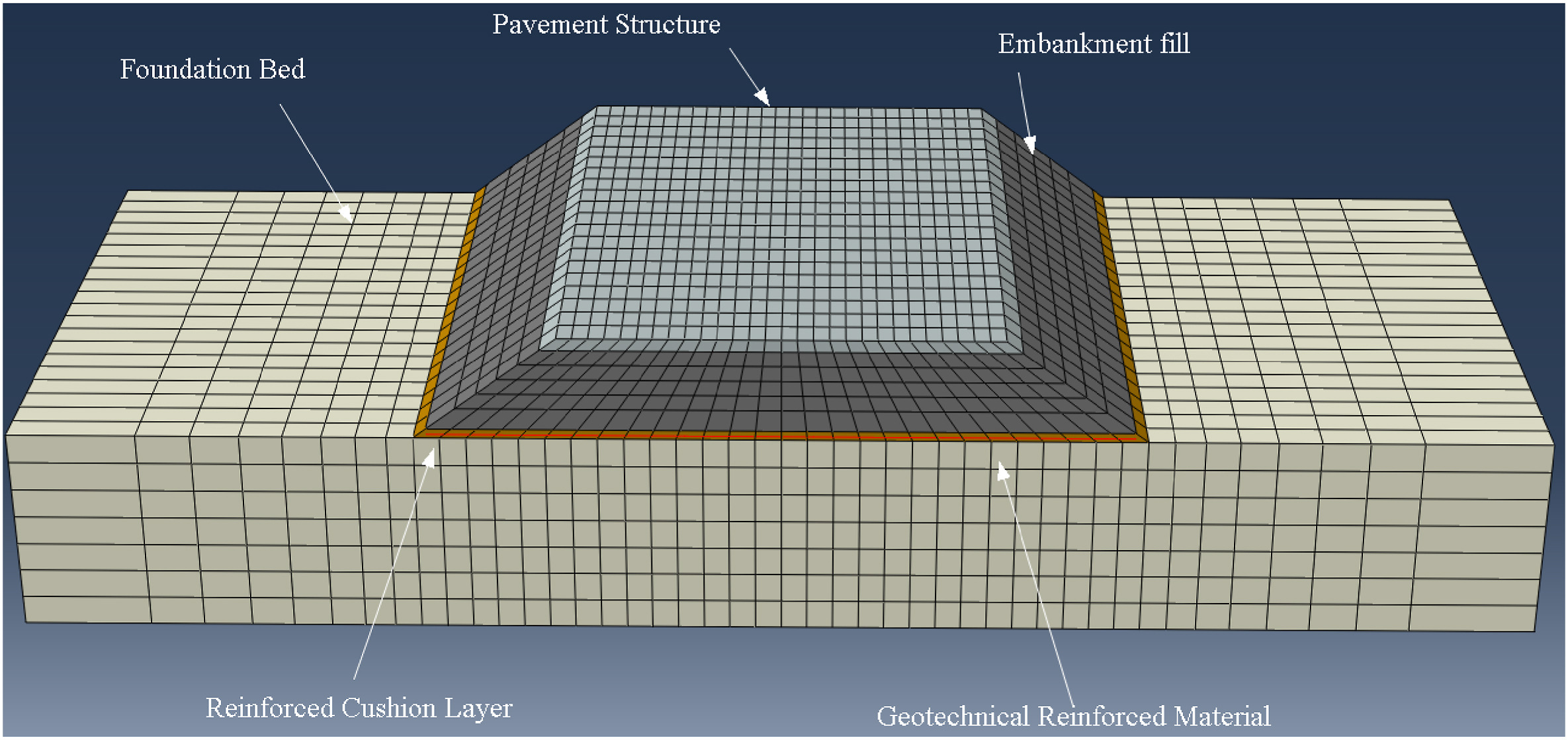
The performance of geosynthetic-reinforced embankments under traffic moving loads is always a hotspot in the geotechnical engineering field. A three-dimensional (3D) model of a geosynthetic-reinforced embankment without drainage consolidation was established using the finite element software ABAQUS. In this model, the traffic loads were simulated by two moving loads of rectangular pattern, and their amplitude, range, and moving speed were realized by a Fortran subroutine. The embankment fill was simulated by an equivalent linear viscoelastic model, which can reflect its viscoelasticity. The geogrid was simulated by the truss element, and the geocell was simulated by the membrane element. Infinite elements were utilized to weaken the boundary effect caused by the model geometry at the boundaries. Validation of the established numerical model was conducted by comparing the predicted deformations in the cross-section of the geosynthetic-reinforced embankment with those from the existing literature. On this basis, the dynamic stress and strain distribution in the pavement structure layer of the geosynthetic-reinforced embankment under a moving load was also analyzed. Finally, a parametric study was conducted to examine the influences of the different types of reinforcement, overload, and the moving load velocity on the geosynthetic-reinforced embankment.
Keywords: Geosynthetic-reinforced layer, Numerical model, Moving load, Embankment, Deformation, Stress
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Xuanming Ding

Dr. Xuanming Ding is engaged in pile foundation dynamics, soft soil foundation reinforcement theory and technology research. He has published 141 papers, one academic monographs. He also participated in the compilation of four national and industry standards and two provincial and ministerial regulations.