JRMGE / Vol 16 / Issue 3
Sliding behaviors of the trapezoidal roof rock block under a lateral dynamic disturbance
Feng Dai, Wancheng Zhu, Min Ren, Shunchuan Wu, Leilei Niu
Show More
a Faculty of Land Resources Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, 650093, China
b Center for Rock Instability and Seismicity Research, Department of Mining Engineering, School of Resource and Civil Engineering, Northeastern University,
Shenyang, 110819, China
2024, 16(3): 741-760. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.10.008
Received: 2023-01-12 / Revised: 2023-08-17 / Accepted: 2023-10-19 / Available online: 2023-12-28
2024, 16(3): 741-760.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.10.008
Received: 2023-01-12
Revised: 2023-08-17
Accepted: 2023-10-19
Available online: 2023-12-28
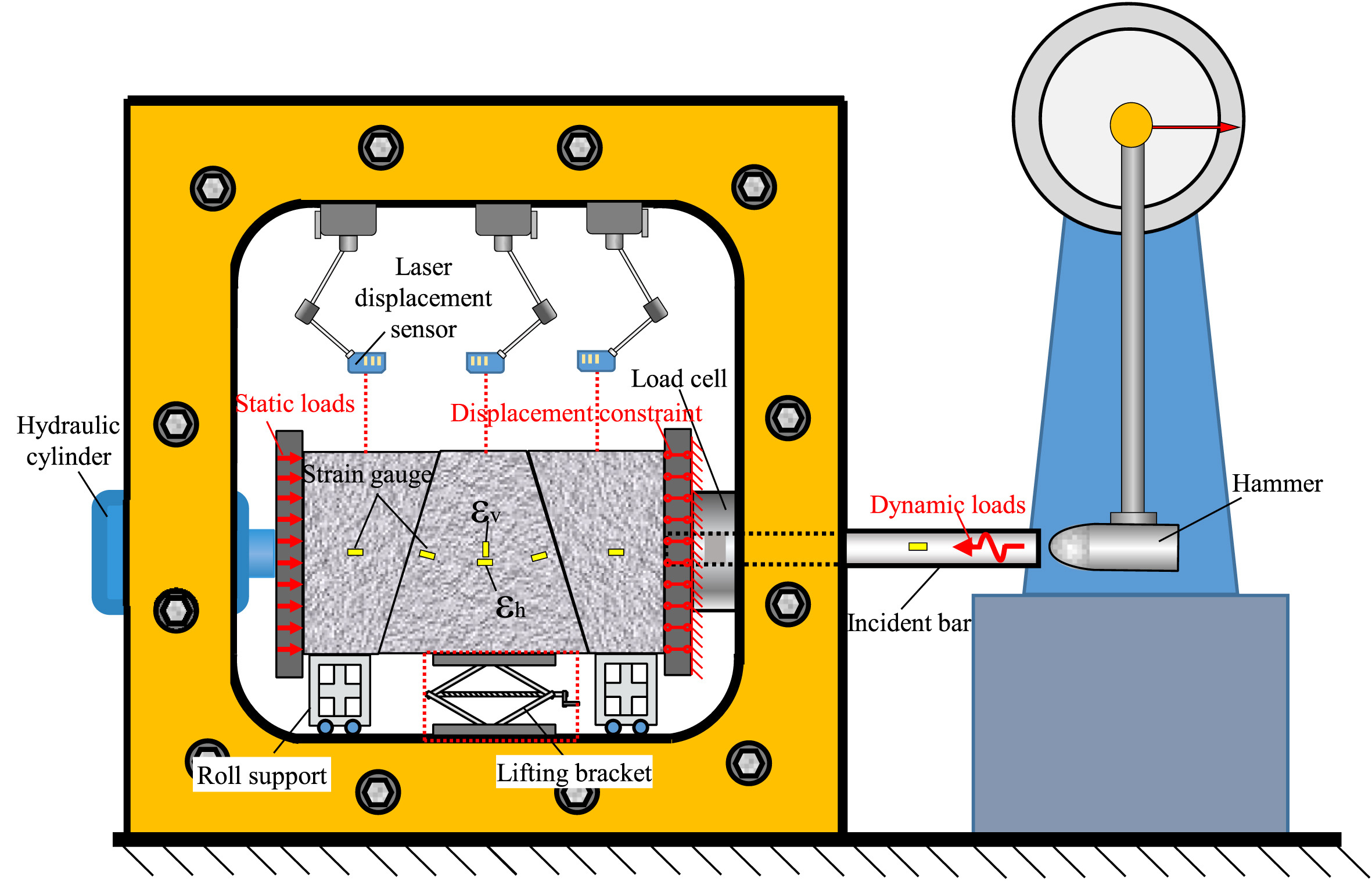
The surrounding rock of underground space is always affected by external dynamic disturbance from the side position, such as blasting vibration from a stope at the same level or seismic waves from adjacent strata. A series of laboratory tests, numerical simulations and theoretical analyses were carried out in this study to disclose the sliding mechanism of roof rock blocks under lateral disturbance. Firstly, the experiments on trapezoidal key block under various clamping loads and disturbance were conducted, followed by numerical simulations using the fast Lagrangian analysis of continua (FLAC3D). Then, based on the conventional wave propagation model and the classical shear-slip constitutive model, a theoretical model was proposed to capture the relative displacement between blocks and the sliding displacement of the key block. The results indicate that the sliding displacement of the key block increased linearly with the disturbance energy and decreased exponentially with the clamping load when the key block was disturbed to slide (without instability). Meanwhile, when the key block was disturbed to fall, two types of instability process may appear as immediate type or delayed type. In addition, the propagation of stress waves in the block system exhibited obvious low-velocity and low-frequency characteristics, resulting in the friction reduction effect appearing at the contact interface, which is the essential reason for the sliding of rock blocks. The results can be applied to practical underground engineering and provide valuable guidance for the early detection and prevention of rock-falling disasters.
Keywords: Lateral dynamic disturbance, Trapezoidal rock block system, Low-velocity and low-frequency wave, Friction reduction effect, Instability mode
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Feng Dai

Feng Dai obtained his BSc degree in Mining Engineering from University of South China in 2014, and his MSc and PhD degrees in Engineering Mechanics from Northeastern University, China, in 2016 and 2022, respectively. He is currently a lecturer at the Faculty of Land Resources Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology in China. His research interests include (1) experimental investigations on the behaviors of rocks under the dynamic disturbance caused by stress waves from blasting or earthquake; and (2) theoretical and technical study on the disaster mechanism and control measures of underground mining collapse disasters. He has been participated in numerous projects funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and been awarded the Excellent Paper Award from the 11th Asian Rock Mechanics Symposium (ARMS11) in 2021. So far, he has published approximately 20 technical papers in rock mechanics.