JRMGE / Vol 14 / Issue 2
A novel approach to structural anisotropy classification for jointed rock masses using theoretical rock quality designation formulation adjusted to joint spacing
Harun Sonmez, Murat Ercanoglu, Gulseren Dagdelenler
Show More
Applied Geology Division, Geological Engineering Department, Faculty of Engineering, Hacettepe University, Beytepe, Ankara, 06800, Turkey
2022, 14(2): 329-345. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.08.009
Received: 2021-02-24 / Revised: 2021-07-21 / Accepted: 2021-08-19 / Available online: 2021-11-01
2022, 14(2): 329-345.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.08.009
Received: 2021-02-24
Revised: 2021-07-21
Accepted: 2021-08-19
Available online: 2021-11-01
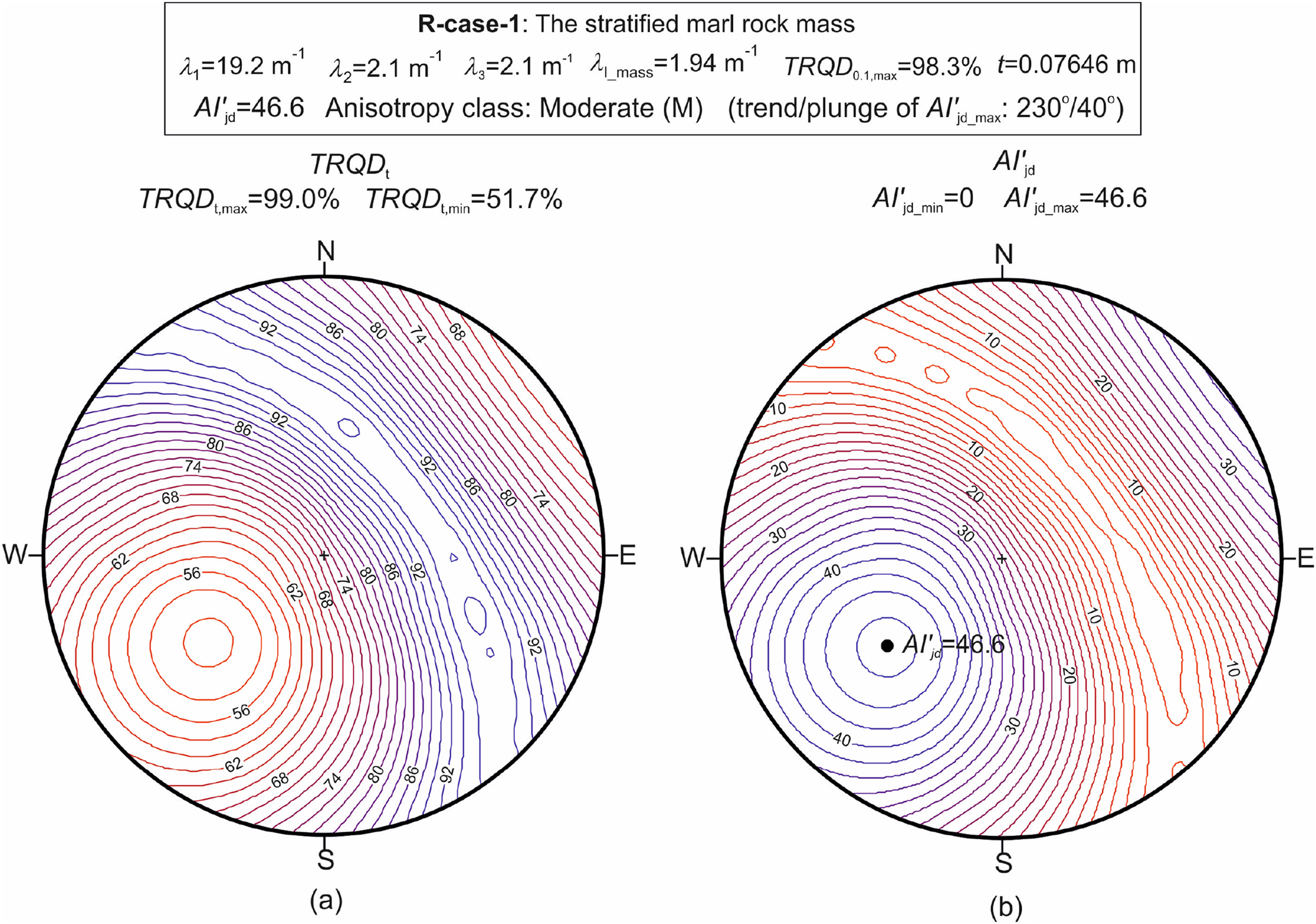
Rock quality designation (RQD) has been considered as a one-dimensional jointing degree property since it should be determined by measuring the core lengths obtained from drilling. Anisotropy index of jointing degree (AIjd) was formulated by Zheng et al. (2018) by considering maximum and minimum values of RQD for a jointed rock medium in three-dimensional space. In accordance with spacing terminology by ISRM (1981), defining the jointing degree for the rock masses composed of extremely closely spaced joints as well as for the rock masses including widely to extremely widely spaced joints is practically impossible because of the use of 10 cm as a threshold value in the conventional form of RQD. To overcome this limitation, theoretical RQD (TRQDt) introduced by Priest and Hudson (1976) can be taken into consideration only when the statistical distribution of discontinuity spacing has a negative exponential distribution. Anisotropy index of the jointing degree was improved using TRQDt which was adjusted to wider joint spacing by considering Priest (1993)'s recommendation on the use of variable threshold value (t) in TRQDt formulation. After applications of the improved anisotropy index of a jointing degree (AIjd′) to hypothetical jointed rock mass cases, the effect of persistency of joints on structural anisotropy of rock mass was introduced to the improved AIjd′ formulation by considering the ratings of persistency of joints as proposed by Bieniawski (1989)'s rock mass rating (RMR) classification. Two real cases were assessed in the stratified marl and the columnar basalt using the weighted anisotropy index of jointing degree (W_AIjd′). A structural anisotropy classification was developed using the RQD classification proposed by Deere (1963). The proposed methodology is capable of defining the structural anisotropy of a rock mass including joint pattern from extremely closely to extremely widely spaced joints.
Keywords: Anisotropy index of jointing degree, Anisotropy of rock mass, Rock mass classification, Jointing degree, Theoretical rock quality designation
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Harun Sonmez
✉️ haruns@hacettepe.edu.tr

Dr. Harun Sonmez received his BSc and MSc degrees in Department of Geological Engineering from Hacettepe University, Turkey, in 1993 and 1996, respectively, and his PhD degree in the same department in 2001. Dr. Sonmez's special areas of research interest are rock mechanics, characterization of jointed rock masses, strength and deformation properties of rock materials, rock masses and block-in-matrix-rocks (bimrocks), stability of deep slopes and their design with remedial measures, monitoring of slope movements, mapping of landslides in terms of susceptibility, hazard and risk assessment, soil mechanics and earthquake triggered soil liquefaction and mapping strategies of soil liquefaction. Dr. Sonmez has also consulting expertise on engineering projects such as dam, tunnel and slope designs and constructions in Turkey and has been involved in many engineering geological projects such as open pit coal mining, landslide mapping, and mineral exploration. Numerous geotechnical softwares were developed by Dr. Sonmez during his research studies such as slope stability, kinematical analyses of rock slopes, artificial neural network, fractal dimension, liquefaction assessment, and monitoring of slopes.