JRMGE / Vol 14 / Issue 4
Slope stability prediction using ensemble learning techniques: A case study in Yunyang County, Chongqing, China
Wengang Zhang, Hongrui Li, Liang Han, Longlong Chen, Lin Wang
Show More
a School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
b Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
c National Joint Engineering Research Center of Geohazards Prevention in the Reservoir Areas, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
2022, 14(4): 1089-1099. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.12.011
Received: 2021-08-25 / Revised: 2021-11-10 / Accepted: 2021-12-21 / Available online: 2022-01-20
2022, 14(4): 1089-1099.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.12.011
Received: 2021-08-25
Revised: 2021-11-10
Accepted: 2021-12-21
Available online: 2022-01-20
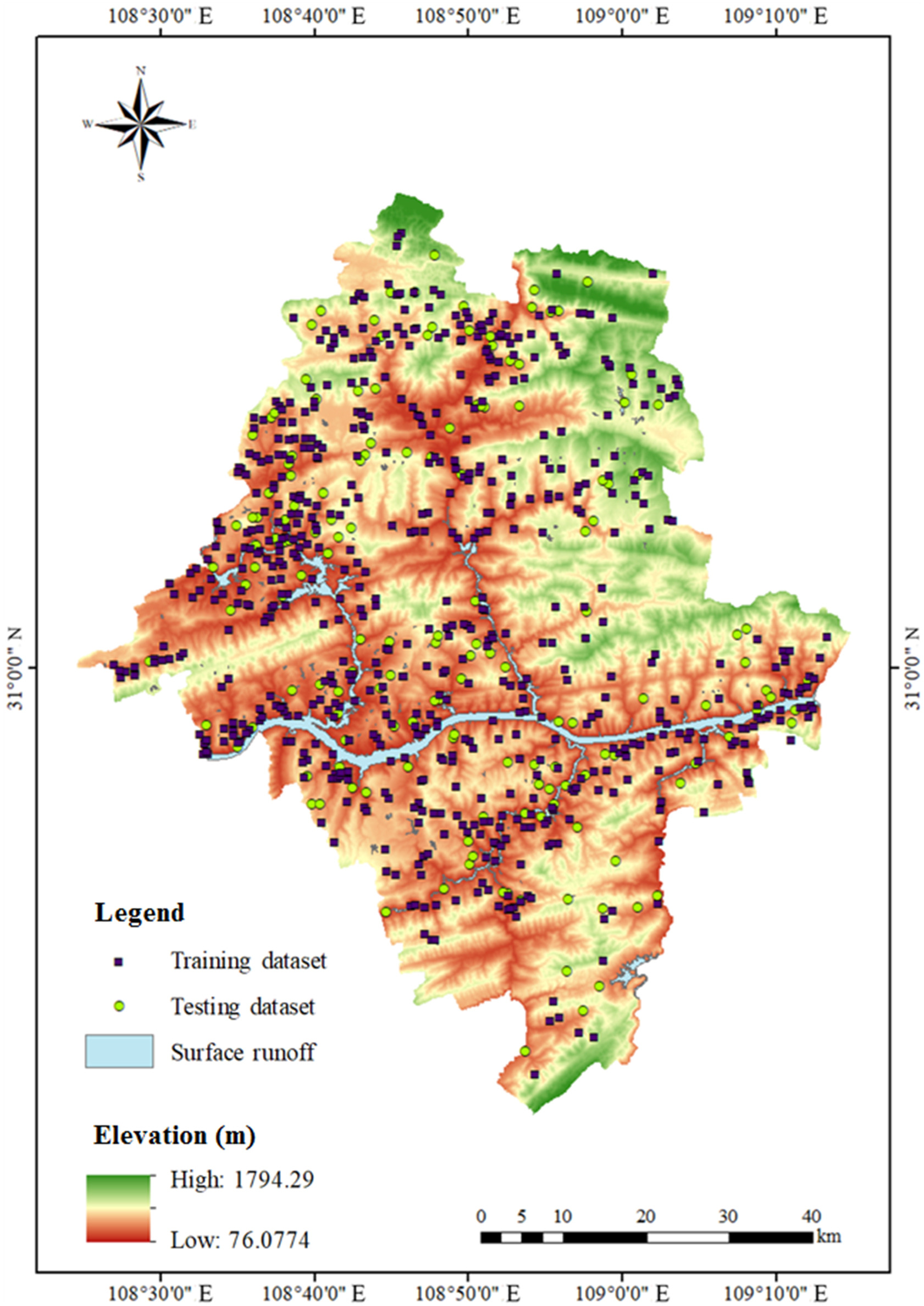
Slope stability prediction plays a significant role in landslide disaster prevention and mitigation. This study develops an ensemble learning-based method to predict the slope stability by introducing the random forest (RF) and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost). As an illustration, the proposed approach is applied to the stability prediction of 786 landslide cases in Yunyang County, Chongqing, China. For comparison, the predictive performance of RF, XGBoost, support vector machine (SVM), and logistic regression (LR) is systematically investigated based on the well-established confusion matrix, which contains the known indices of recall rate, precision, and accuracy. Furthermore, the feature importance of the 12 influencing variables is also explored. Results show that the accuracy of the XGBoost and RF for both the training and testing data is superior to that of SVM and LR, revealing the superiority of the ensemble learning models (i.e. XGBoost and RF) in the slope stability prediction of Yunyang County. Among the 12 influencing factors, the profile shape is the most important one. The proposed ensemble learning-based method offers a promising way to rationally capture the slope status. It can be extended to the prediction of slope stability of other landslide-prone areas of interest.
Keywords: Machine learning, Slope stability, Yunyang county, Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost), Random forest (RF)
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Prof. Wengang Zhang
zhangwg@cqu.edu.cn

Wengang Zhang is currently full professor in School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, China. He obtained his BSc and MSc degrees from the Hohai University in China and his PhD from Nanyang Technological University, Singapore. He is now the member of the International Society for society Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering TC304 (Reliability), TC309 (Machine Learning), TC219 (System Performance of Geotechnical Structures) and TC222 (Building Information Modelling and Digital Twins). Dr. Zhang has been selected as the World's Top 2% Scientists in 2020 and 2021. He received 2021 Underground Space Outstanding Paper Award, Computers and Geotechnics Sloan Outstanding Paper Award, Tunnelling and Underground Construction Society (Singapore) Hulme Best Paper Award and the Best Referees 2020 of Geoscience Frontiers. He served as Associate Editor for Geoscience Frontiers, editorial board member of Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering and Georisk.