JRMGE / Vol 16 / Issue 3
Experimental investigation on the permeability of gap-graded soil due to horizontal suffusion considering boundary effect
Xuwei Wang, Yeshuang Xu
Show More
a State Key Laboratory of Ocean Engineering, School of Naval Architecture, Ocean, and Civil Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, 200240, China
b Shanghai Key Laboratory for Digital Maintenance of Buildings and Infrastructure, Department of Civil Engineering, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai,
200240, China
2024, 16(3): 1072-1084. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.08.017
Received: 2023-01-06 / Revised: 2023-05-12 / Accepted: 2023-08-14 / Available online: 2023-11-22
2024, 16(3): 1072-1084.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.08.017
Received: 2023-01-06
Revised: 2023-05-12
Accepted: 2023-08-14
Available online: 2023-11-22
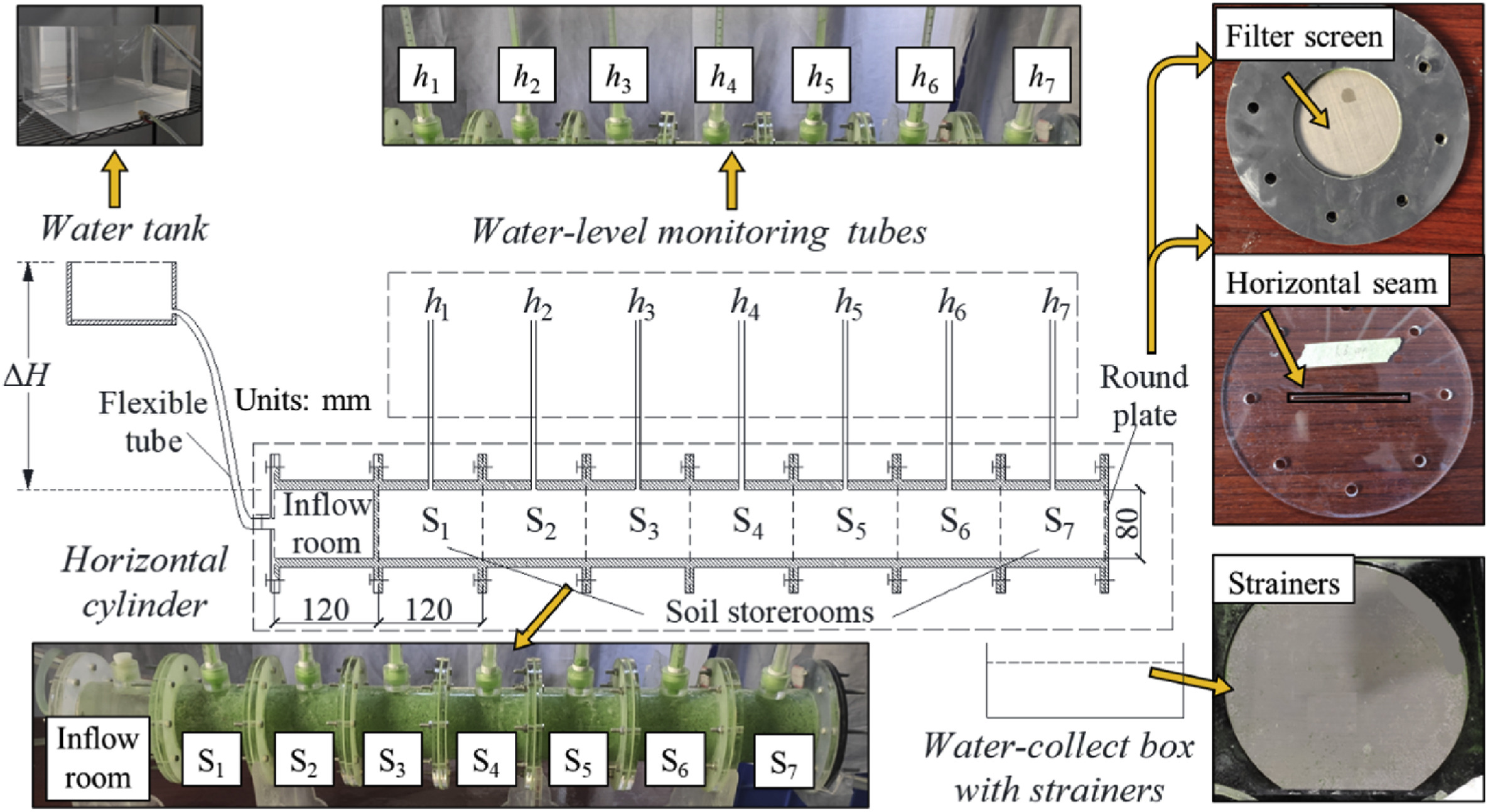
The boundary condition is a crucial factor affecting the permeability variation due to suffusion. An experimental investigation on the permeability of gap-graded soil due to horizontal suffusion considering the boundary effect is conducted, where the hydraulic head difference (ΔH) varies, and the boundary includes non-loss and soil-loss conditions. Soil samples are filled into seven soil storerooms connected in turn. After evaluation, the variation in content of fine sand (ΔRf) and the hydraulic conductivity of soils in each storeroom (Ci) are analyzed. In the non-loss test, the soil sample filling area is divided into runoff, transited, and accumulated areas according to the negative or positive ΔRf values. ΔRf increases from negative to positive along the seepage path, and Ci decreases from runoff area to transited area and then rebounds in accumulated area. In the soil-loss test, all soil sample filling areas belong to the runoff area, where the gentle-loss, strengthened-loss, and alleviated-loss parts are further divided. ΔRf decreases from the gentle-loss part to the strengthened-loss part and then rebounds in the alleviated-loss part, and Ci increases and then decreases along the seepage path. The relationship between ΔRf and Ci is different with the boundary condition. Ci exponentially decreases with ΔRf in the non-loss test and increases with ΔRf generally in the soil-loss test.
Keywords: Suffusion, Permeability, Experimental investigation, Boundary effect, Horizontal seepage
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Yeshuang Xu
✉️ xuyeshuang@sjtu.edu.cn

Yeshuang Xu obtained her BSc degree in Civil Engineering from Suzhou University of Science and Technology, China, in 1999, and her MSc degree and PhD in Civil Engineering from Shanghai Jiao Tong University in 2006 and 2010, respectively. She was affiliated as assistant professor from 2010 to 2013 and associate professor since 2014 with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China. Her research interests include (1) Mechanism and simulation study on land subsidence; and (2) Research on engineering, geological and environmental problems related to groundwater seepage. She has been participated in some projects funded by National Nature Science Foundation of China.