JRMGE / Vol 16 / Issue 3
Limit state analysis of rigid retaining structures against seismically induced passive failure in heterogeneous soils
Jianfeng Zhou, Changbing Qin
Show More
a College of Civil Engineering, Huaqiao University, Xiamen, 362021, China
b School of Civil Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
c Key Laboratory of New Technology for Construction of Cities in Mountain Area, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
d National Joint Engineering Research Center of Geohazards Prevention in the Reservoir Areas, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400045, China
2024, 16(3): 1095-1105. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.009
Received: 2022-12-31 / Revised: 2023-03-20 / Accepted: 2023-04-12 / Available online: 2023-06-04
2024, 16(3): 1095-1105.
doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.009
Received: 2022-12-31
Revised: 2023-03-20
Accepted: 2023-04-12
Available online: 2023-06-04
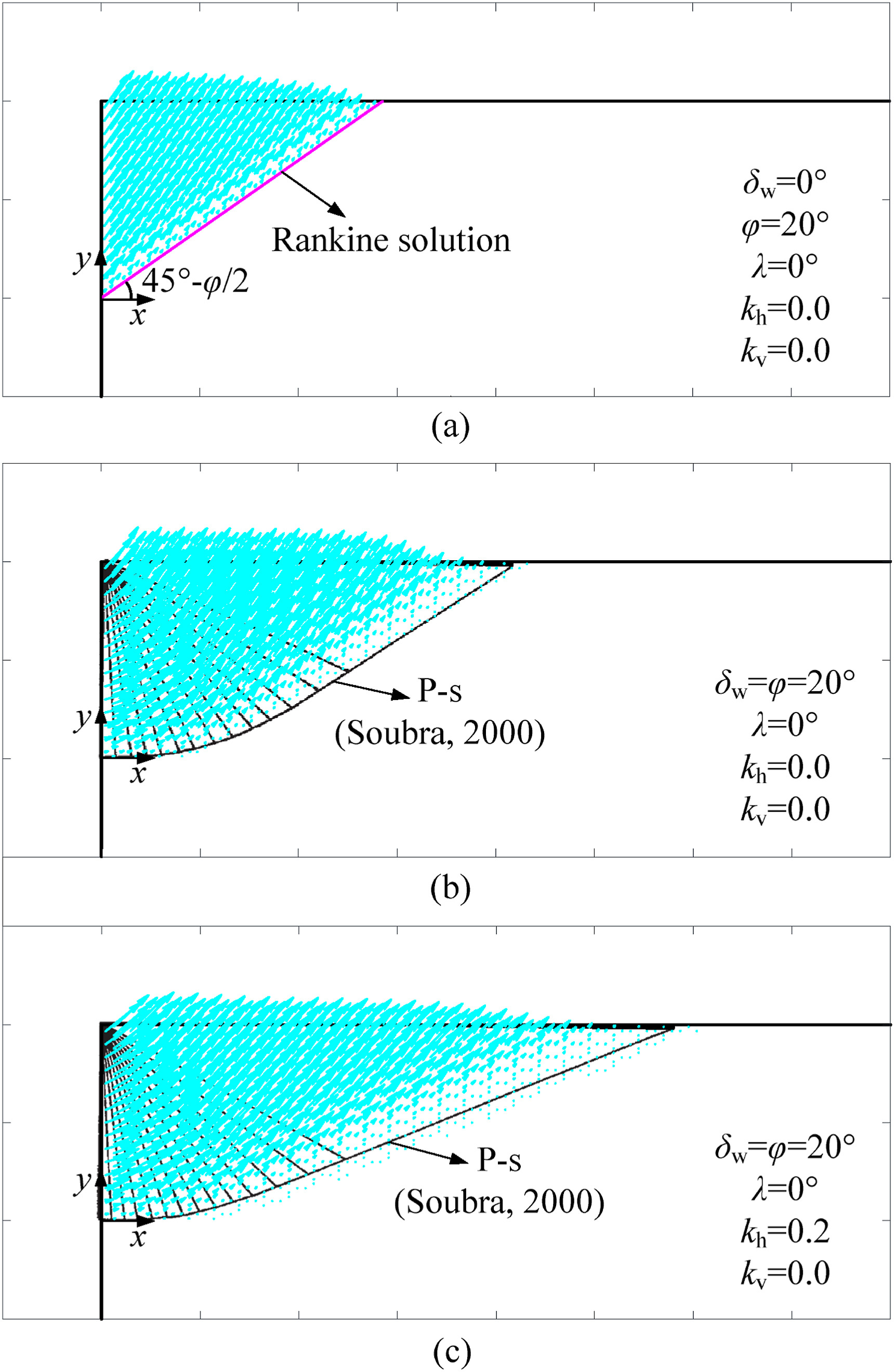
Soils are not necessarily uniform and may present linearly varied or layered characteristics, for example the backfilled soils behind rigid retaining walls. In the presence of large lateral thrust imposed by arch bridge, passive soil failure is possible. A reliable prediction of passive earth pressure for the design of such wall is challenging in complicated soil strata, when adopting the conventional limit analysis method. In order to overcome the challenge for generating a kinematically admissible velocity field and a statically allowable stress field, finite element method is incorporated into limit analysis, forming finite-element upper-bound (FEUB) and finite-element lower-bound (FELB) methods. Pseudo-static, original and modified pseudo-dynamic approaches are adopted to represent seismic acceleration inputs. After generating feasible velocity and stress fields within discretized elements based on specific criteria, FEUB and FELB formulations of seismic passive earth pressure (coefficient KP) can be derived from work rate balance equation and stress equilibrium. Resorting to an interior point algorithm, optimal upper and lower bound solutions are obtained. The proposed FEUB and FELB procedures are well validated by limit equilibrium as well as lower-bound and kinematic analyses. Parametric studies are carried out to investigate the effects of influential factors on seismic KP. Notably, true solution of KP is well estimated based on less than 5% difference between FEUB and FELB solutions under such complex scenarios.
Keywords: Retaining wall, Passive earth pressure, Earthquakes, Finite-element limit-analysis methods
Article Data
Author(s) Information
Changbing Qin

Changbing Qin received his BEng degree from Zhengzhou University in 2012, MEng degree from Central South University in 2015, and PhD degree from National University of Singapore in 2019. He is currently working as a Professor at the Chongqing University. His research interest includes (1) Slope engineering mainly on stability analyses, landslides, and debris flow, and (2) Tunnel engineering mainly on tunnel roof and face analyses.