-
Coalbursts in China: Theory, practice and management
Yishan Pan, Yimin Song, Hao Luo, Yonghui Xiao
2024, 16(1): 1-25. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.11.003
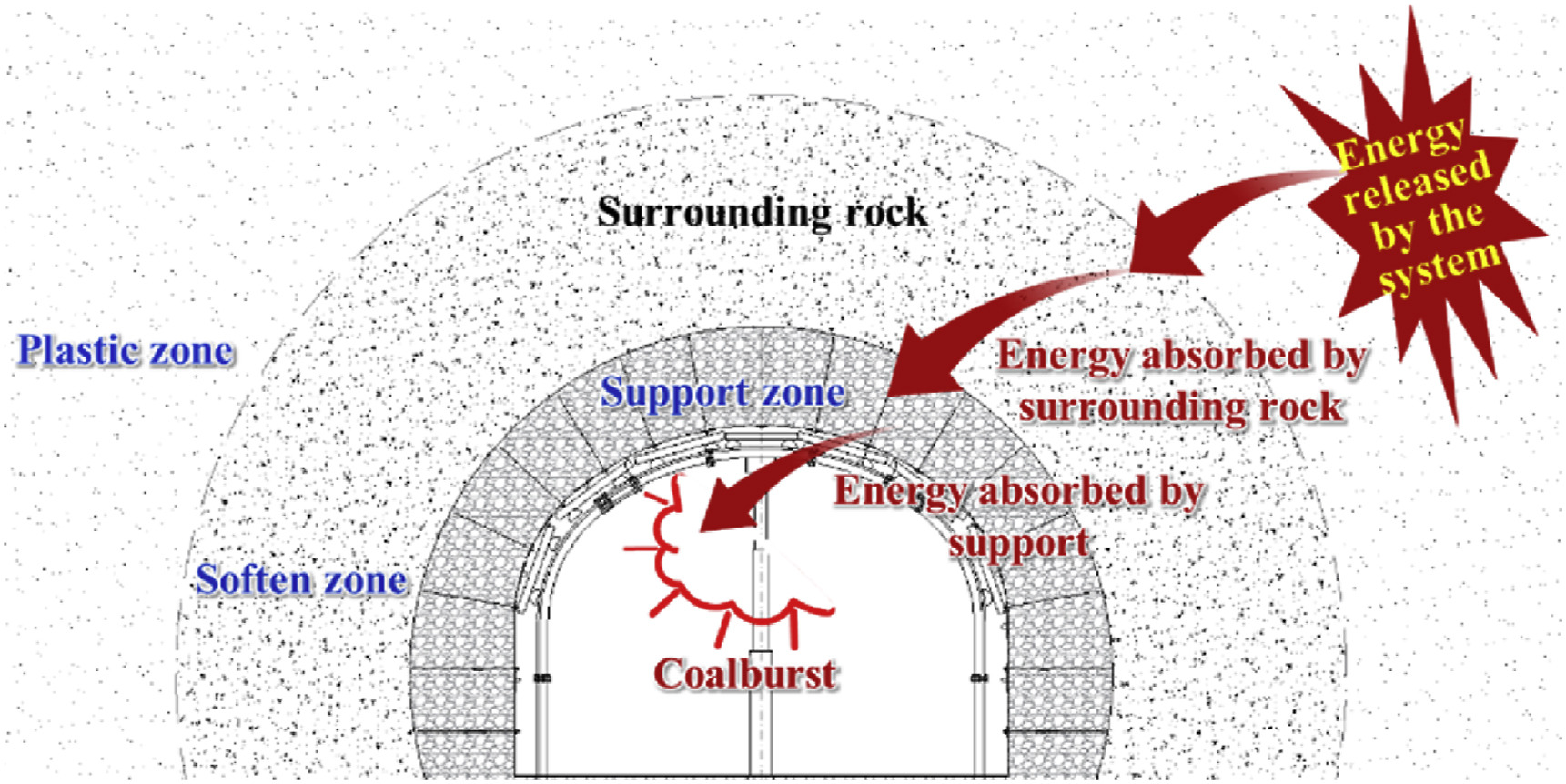
Abstract: Coalburst is one of the most serious disasters that threaten the safe production of coal mines, and this disaster is particularly serious in China. This paper presents an overview of coalbursts in China since 1980s. From the "stress and energy" and "regional and local" perspectives, the achievements in the theory, practice and management of coalbursts in China are systematically summarized. A theoretical system of coShow FiguresCoalburst is one of the most serious disasters that threaten the safe production of coal mines, and this disaster is particularly serious in China. This paper presents an overview of coalbursts in China since 1980s. From the "stress and energy" and "regional and local" perspectives, the achievements in the theory, practice and management of coalbursts in China are systematically summarized. A theoretical system of coalbursts has been formed to reveal the deformational behavior of coalbursts and explain the mechanism of coalbursts. The occurrence conditions of coalbursts are put forward and the critical stress is obtained. The stress index method for risk evaluation of coalbursts before mining is proposed, and the deformation localization prediction method of coalbursts is put forward. The relationship between energy release and absorption in the process of coalbursts is found, and the prevention and control methods of coalbursts, including the regional method, the local method and support, are presented. The safety evaluation index of coalburst prevention and control is put forward. The integrated prevention and control method for coal and gas outbursts is proposed. The prevention and control technology and equipment of coalbursts have also been developed. Amongst them, the distribution law of the critical stress in China coalburst mines is discovered. The technology and equipment for monitoring, prevention and control of coalbursts, as well as for integrated prevention and control of combined coalbursts and other disasters, have been developed. The energy-absorbing and coalburst-preventing support technology for roadways is invented, and key engineering parameters of coalburst prevention and control are pointed out. In China, coalburst prevention and control laws and standards have been developed. Technical standards for coalbursts are formulated, statute and regulations for coal mines are established, and regulatory documents are promoted.
[...]Read more. -
Insights into carbon dioxide sequestration into coal seams through coupled gas flow-adsorption-deformation modelling
Hywel Thomas, Min Chen
2024, 16(1): 26-40. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.11.004
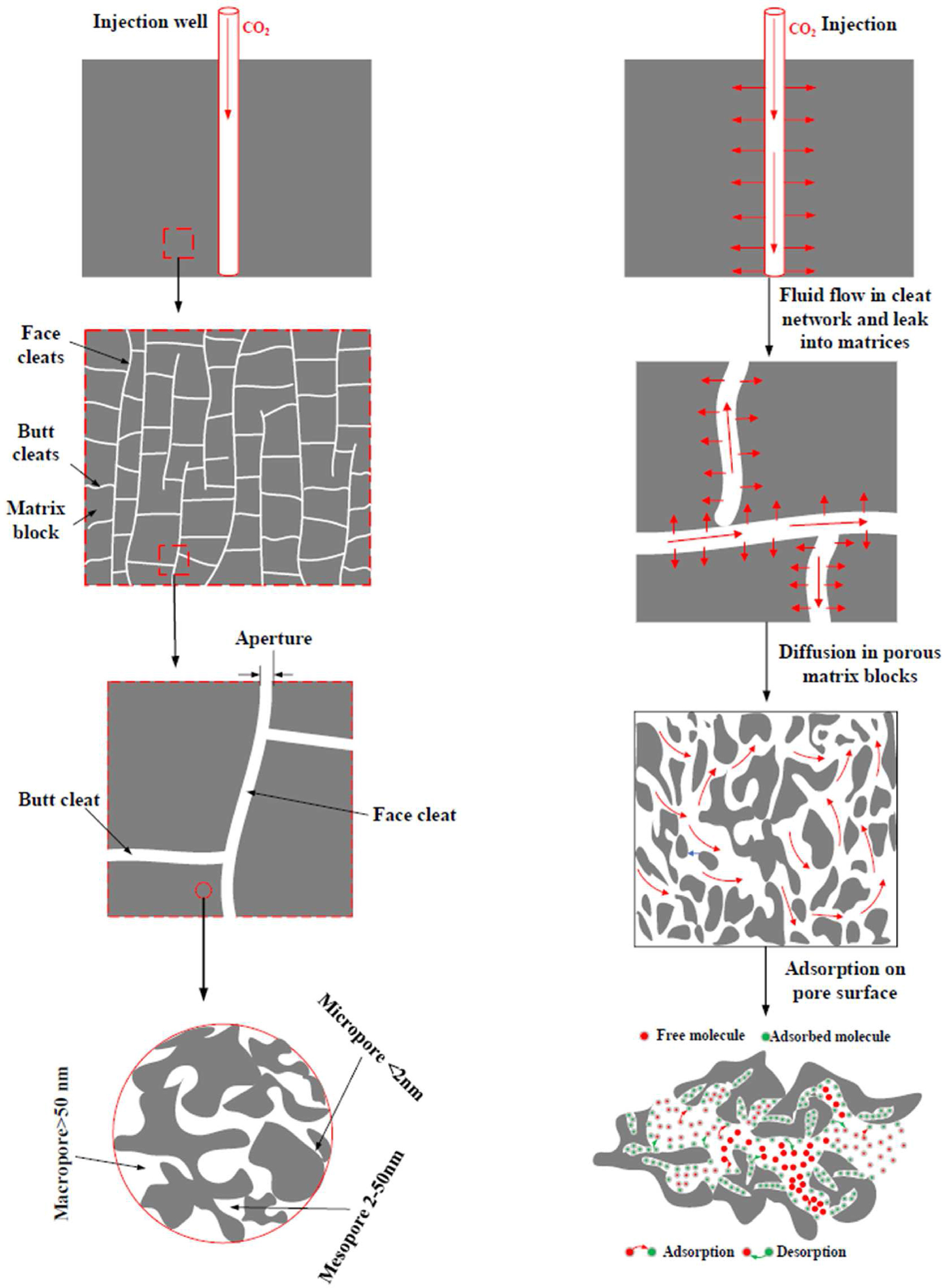
Abstract: Injecting carbon dioxide (CO2) into coal seams may unlock substantial carbon sequestration potential. Since the coal acts like a carbon filter, it can preferentially absorb significant amounts of CO2. To explore this further, desorption of the adsorbed gas due to pressure drop is investigated in this paper, to achieve an improved understanding of the long-term fate of injected CO2 during post-injection period. This pShow FiguresInjecting carbon dioxide (CO2) into coal seams may unlock substantial carbon sequestration potential. Since the coal acts like a carbon filter, it can preferentially absorb significant amounts of CO2. To explore this further, desorption of the adsorbed gas due to pressure drop is investigated in this paper, to achieve an improved understanding of the long-term fate of injected CO2 during post-injection period. This paper presents a dual porosity model coupling gas flow, adsorption and geomechanics for studying coupled processes and effectiveness of CO2 sequestration in coals. A new adsorption−desorption model derived based on thermodynamics is incorporated, particularly, the desorption hysteresis is considered. The reliability of the proposed adsorption-desorption isotherm is examined via validation tests. It is indicated that occurrence of desorption hysteresis is attributed to the adsorption-induced pore deformation. After injection ceases, the injected gas continues to propagate further from the injection well, while the pressure in the vicinity of the injection well experiences a significant drop. Although the adsorbed gas near the well also decreases, this decrease is less compared to that in pressure because of desorption hysteresis. The unceasing spread of CO22 and drops of pressure and adsorbed gas depend on the degree of desorption hysteresis and heterogeneity of coals, which should be considered when designing CO2 sequestration into coal seams.
[...]Read more. -
Tensile strength and failure behavior of rock-mortar interfaces: Direct and indirect measurements
Ghasem Shams, Patrice Rivard, Omid Moradian
2024, 16(1): 41-55. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.013
Abstract: The tensile strength at the rock-concrete interface is one of the crucial factors controlling the failure mechanisms of structures, such as concrete gravity dams. Despite the critical importance of the failure mechanism and tensile strength of rock-concrete interfaces, understanding of these factors remains very limited. This study investigated the tensile strength and fracturing processes at rock-mortar interfaces sShow FiguresThe tensile strength at the rock-concrete interface is one of the crucial factors controlling the failure mechanisms of structures, such as concrete gravity dams. Despite the critical importance of the failure mechanism and tensile strength of rock-concrete interfaces, understanding of these factors remains very limited. This study investigated the tensile strength and fracturing processes at rock-mortar interfaces subjected to direct and indirect tensile loadings. Digital image correlation (DIC) and acoustic emission (AE) techniques were used to monitor the failure mechanisms of specimens subjected to direct tension and indirect loading (Brazilian tests). The results indicated that the direct tensile strength of the rock-mortar specimens was lower than their indirect tensile strength, with a direct/indirect tensile strength ratio of 65%. DIC strain field data and moment tensor inversions (MTI) of AE events indicated that a significant number of shear microcracks occurred in the specimens subjected to the Brazilian test. The presence of these shear microcracks, which require more energy to break, resulted in a higher tensile strength during the Brazilian tests. In contrast, microcracks were predominantly tensile in specimens subjected to direct tension, leading to a lower tensile strength. Spatiotemporal monitoring of the cracking processes in the rock-mortar interfaces revealed that they show AE precursors before failure under the Brazilian test, whereas they show a minimal number of AE events before failure under direct tension. Due to different microcracking mechanisms, specimens tested under Brazilian tests showed lower roughness with flatter fracture surfaces than those tested under direct tension with jagged and rough fracture surfaces. The results of this study shed light on better understanding the micromechanics of damage in the rock-concrete interfaces for a safer design of engineering structures.
[...]Read more. -
Failure transition of shear-to-dilation band of rock salt under triaxial stresses
Jianfeng Liu, Xiaosong Qiu, Jianxiong Yang, Chao Liang, Jingjing Dai, Yu Bian
2024, 16(1): 56-64. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.015
Abstract: Great potential of underground gas/energy storage in salt caverns seems to be a promising solution to support renewable energy. In the underground storage method, the operating cycle unfortunately may reach up to daily or even hourly, which generates complicated pressures on the salt cavern. Furthermore, the mechanical behavior of rock salt may change and present distinct failure characteristics under different stresShow FiguresGreat potential of underground gas/energy storage in salt caverns seems to be a promising solution to support renewable energy. In the underground storage method, the operating cycle unfortunately may reach up to daily or even hourly, which generates complicated pressures on the salt cavern. Furthermore, the mechanical behavior of rock salt may change and present distinct failure characteristics under different stress states, which affects the performance of salt cavern during the time period of full service. To reproduce a similar loading condition on the cavern surrounding rock mass, the cyclic triaxial loading/unloading tests are performed on the rock salt to explore the mechanical transition behavior and failure characteristics under different confinement. Experimental results show that the rock salt samples present a diffused shear failure band with significant bulges at certain locations in low confining pressure conditions (e.g. 5 MPa, 10 MPa and 15 MPa), which is closely related to crystal misorientation and grain boundary sliding. Under the elevated confinement (e.g. 20 MPa, 30 MPa and 40 MPa), the dilation band dominates the failure mechanism, where the large-size halite crystals are crushed to be smaller size and new pores are developing. The failure transition mechanism revealed in the paper provides additional insight into the mechanical performance of salt caverns influenced by complicated stress states.
[...]Read more. -
A performance-based hybrid deep learning model for predicting TBM advance rate using Attention-ResNet-LSTM
Sihao Yu, Zixin Zhang, Shuaifeng Wang, Xin Huang, Qinghua Lei
2024, 16(1): 65-80. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.06.010
Abstract: The technology of tunnel boring machine (TBM) has been widely applied for underground construction worldwide; however, how to ensure the TBM tunneling process safe and efficient remains a major concern. Advance rate is a key parameter of TBM operation and reflects the TBM-ground interaction, for which a reliable prediction helps optimize the TBM performance. Here, we develop a hybrid neural network model, called AtteShow FiguresThe technology of tunnel boring machine (TBM) has been widely applied for underground construction worldwide; however, how to ensure the TBM tunneling process safe and efficient remains a major concern. Advance rate is a key parameter of TBM operation and reflects the TBM-ground interaction, for which a reliable prediction helps optimize the TBM performance. Here, we develop a hybrid neural network model, called Attention-ResNet-LSTM, for accurate prediction of the TBM advance rate. A database including geological properties and TBM operational parameters from the Yangtze River Natural Gas Pipeline Project is used to train and test this deep learning model. The evolutionary polynomial regression method is adopted to aid the selection of input parameters. The results of numerical experiments show that our Attention-ResNet-LSTM model outperforms other commonly-used intelligent models with a lower root mean square error and a lower mean absolute percentage error. Further, parametric analyses are conducted to explore the effects of the sequence length of historical data and the model architecture on the prediction accuracy. A correlation analysis between the input and output parameters is also implemented to provide guidance for adjusting relevant TBM operational parameters. The performance of our hybrid intelligent model is demonstrated in a case study of TBM tunneling through a complex ground with variable strata. Finally, data collected from the Baimang River Tunnel Project in Shenzhen of China are used to further test the generalization of our model. The results indicate that, compared to the conventional ResNet-LSTM model, our model has a better predictive capability for scenarios with unknown datasets due to its self-adaptive characteristic.
[...]Read more. -
Numerical investigation of geostress influence on the grouting reinforcement effectiveness of tunnel surrounding rock mass in fault fracture zones
Xiangyu Xu, Zhijun Wu, Lei Weng, Zhaofei Chu, Quansheng Liu, Yuan Zhou
2024, 16(1): 81-101. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.011
Abstract: Grouting is a widely used approach to reinforce broken surrounding rock mass during the construction of underground tunnels in fault fracture zones, and its reinforcement effectiveness is highly affected by geostress. In this study, a numerical manifold method (NMM) based simulator has been developed to examine the impact of geostress conditions on grouting reinforcement during tunnel excavation. To develop this simuShow FiguresGrouting is a widely used approach to reinforce broken surrounding rock mass during the construction of underground tunnels in fault fracture zones, and its reinforcement effectiveness is highly affected by geostress. In this study, a numerical manifold method (NMM) based simulator has been developed to examine the impact of geostress conditions on grouting reinforcement during tunnel excavation. To develop this simulator, a detection technique for identifying slurry migration channels and an improved fluid-solid coupling (F–S) framework, which considers the influence of fracture properties and geostress states, is developed and incorporated into a zero-thickness cohesive element (ZE) based NMM (Co-NMM) for simulating tunnel excavation. Additionally, to simulate coagulation of injected slurry, a bonding repair algorithm is further proposed based on the ZE model. To verify the accuracy of the proposed simulator, a series of simulations about slurry migration in single fractures and fracture networks are numerically reproduced, and the results align well with analytical and laboratory test results. Furthermore, these numerical results show that neglecting the influence of geostress condition can lead to a serious overestimation of slurry migration range and reinforcement effectiveness. After validations, a series of simulations about tunnel grouting reinforcement and tunnel excavation in fault fracture zones with varying fracture densities under different geostress conditions are conducted. Based on these simulations, the influence of geostress conditions and the optimization of grouting schemes are discussed.
[...]Read more. -
Assessment of compressive strength of jet grouting by machine learning
Esteban Díaz, Edgar Leonardo Salamanca-Medina, Roberto Tomás
2024, 16(1): 102-111. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.008
Abstract: Jet grouting is one of the most popular soil improvement techniques, but its design usually involves great uncertainties that can lead to economic cost overruns in construction projects. The high dispersion in the properties of the improved material leads to designers assuming a conservative, arbitrary and unjustified strength, which is even sometimes subjected to the results of the test fields. The present paper preShow FiguresJet grouting is one of the most popular soil improvement techniques, but its design usually involves great uncertainties that can lead to economic cost overruns in construction projects. The high dispersion in the properties of the improved material leads to designers assuming a conservative, arbitrary and unjustified strength, which is even sometimes subjected to the results of the test fields. The present paper presents an approach for prediction of the uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) of jet grouting columns based on the analysis of several machine learning algorithms on a database of 854 results mainly collected from different research papers. The selected machine learning model (extremely randomized trees) relates the soil type and various parameters of the technique to the value of the compressive strength. Despite the complex mechanism that surrounds the jet grouting process, evidenced by the high dispersion and low correlation of the variables studied, the trained model allows to optimally predict the values of compressive strength with a significant improvement with respect to the existing works. Consequently, this work proposes for the first time a reliable and easily applicable approach for estimation of the compressive strength of jet grouting columns.
[...]Read more. -
Investigation of the block toppling evolution of a layered model slope by centrifuge test and discrete element modeling
Leilei Jin, Hongkai Dong, Fei Ye, Yufeng Wei, Jianfeng Liu, Changkui Wang
2024, 16(1): 112-122. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.019
Abstract: Primary toppling usually occurs in layered rock slopes with large anti-dip angles. In this paper, the block toppling evolution was explored using a large-scale centrifuge system. Each block column in the layered model slope was made of cement mortar. Some artificial cracks perpendicular to the block column were prefabricated. Strain gages, displacement gages, and high-speed camera measurements were employed to monitoShow FiguresPrimary toppling usually occurs in layered rock slopes with large anti-dip angles. In this paper, the block toppling evolution was explored using a large-scale centrifuge system. Each block column in the layered model slope was made of cement mortar. Some artificial cracks perpendicular to the block column were prefabricated. Strain gages, displacement gages, and high-speed camera measurements were employed to monitor the deformation and failure processes of the model slope. The centrifuge test results show that the block toppling evolution can be divided into seven stages, i.e. layer compression, formation of major tensile crack, reverse bending of the block column, closure of major tensile crack, strong bending of the block column, formation of failure zone, and complete failure. Block toppling is characterized by sudden large deformation and occurs in stages. The wedge-shaped cracks in the model incline towards the slope. Experimental observations show that block toppling is mainly caused by bending failure rather than by shear failure. The tensile strength also plays a key factor in the evolution of block toppling. The simulation results from discrete element method (DEM) is in line with the testing results. Tensile stress exists at the backside of rock column during toppling deformation. Stress concentration results in the fragmented rock column and its degree is the most significant at the slope toe.
[...]Read more. -
A gated recurrent unit model to predict Poisson's ratio using deep learning
Fahd Saeed Alakbari, Mysara Eissa Mohyaldinn, Mohammed Abdalla Ayoub, Ibnelwaleed A. Hussein, Ali Samer Muhsan, Syahrir Ridha, Abdullah Abduljabbar Salih
2024, 16(1): 123-135. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.012
Abstract: Static Poisson's ratio (νs) is crucial for determining geomechanical properties in petroleum applications, namely sand production. Some models have been used to predict νs; however, the published models were limited to specific data ranges with an average absolute percentage relative error (AAPRE) of more than 10%. The published gated recurrent unit (GRU) models do not consider trend analysis to show physical bShow FiguresStatic Poisson's ratio (νs) is crucial for determining geomechanical properties in petroleum applications, namely sand production. Some models have been used to predict νs; however, the published models were limited to specific data ranges with an average absolute percentage relative error (AAPRE) of more than 10%. The published gated recurrent unit (GRU) models do not consider trend analysis to show physical behaviors. In this study, we aim to develop a GRU model using trend analysis and three inputs for predicting νs based on a broad range of data, νs (value of 0.1627–0.4492), bulk formation density (RHOB) (0.315–2.994 g/mL), compressional time (DTc) (44.43–186.9 μs/ft), and shear time (DTs) (72.9–341.2 μs/ft). The GRU model was evaluated using different approaches, including statistical error analyses. The GRU model showed the proper trends, and the model data ranges were wider than previous ones. The GRU model has the largest correlation coefficient (R) of 0.967 and the lowest AAPRE, average percent relative error (APRE), root mean square error (RMSE), and standard deviation (SD) of 3.228%, −1.054%, 4.389, and 0.013, respectively, compared to other models. The GRU model has a high accuracy for the different datasets: training, validation, testing, and the whole datasets with R and AAPRE values were 0.981 and 2.601%, 0.966 and 3.274%, 0.967 and 3.228%, and 0.977 and 2.861%, respectively. The group error analyses of all inputs show that the GRU model has less than 5% AAPRE for all input ranges, which is superior to other models that have different AAPRE values of more than 10% at various ranges of inputs.
[...]Read more. -
Experimental study on the effect of water absorption level on rockburst occurrence of sandstone
Dongqiao Liu, Jie Sun, Pengfei He, Manchao He, Binghao Cao, Yuanyuan Yang
2024, 16(1): 136-152. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.06.019
Abstract: To investigate the mechanism of rockburst prevention by spraying water onto the surrounding rocks, 15 experiments are performed considering different water absorption levels on a single face. High-speed photography and acoustic emission (AE) system are used to monitor the rockburst process. The effect of water on sandstone rockburst and the prevention mechanism of water on sandstone rockburst are analyzed from the peShow FiguresTo investigate the mechanism of rockburst prevention by spraying water onto the surrounding rocks, 15 experiments are performed considering different water absorption levels on a single face. High-speed photography and acoustic emission (AE) system are used to monitor the rockburst process. The effect of water on sandstone rockburst and the prevention mechanism of water on sandstone rockburst are analyzed from the perspective of energy and failure mode. The results show that the higher the absorption degree, the lower the intensity of the rockburst after absorbing water on single side of sandstone. This is reflected in the fact that with the increase in the water absorption level, the ejection velocity of rockburst fragments is smaller, the depth of the rockburst pit is shallower, and the AE energy is smaller. Under the water absorption level of 100%, the magnitude of rockburst intensity changes from medium to slight. The prevention mechanism of water on sandstone rockburst is that water reduces the capacity of sandstone to store strain energy and accelerates the expansion of shear cracks, which is not conducive to the occurrence of plate cracking before rockburst, and destroys the conditions for rockburst incubation.
[...]Read more. -
A three-dimensional feature extraction-based method for coal cleat characterization using X-ray μCT and its application to a Bowen Basin coal specimen
Yulai Zhang, Matthew Tsang, Mark Knackstedt, Michael Turner, Shane Latham, Euan Macaulay, Rhys Pitchers
2024, 16(1): 153-166. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.001
Abstract: Cleats are the dominant micro-fracture network controlling the macro-mechanical behavior of coal. Improved understanding of the spatial characteristics of cleat networks is therefore important to the coal mining industry. Discrete fracture networks (DFNs) are increasingly used in engineering analyses to spatially model fractures at various scales. The reliability of coal DFNs largely depends on the confidence in theShow FiguresCleats are the dominant micro-fracture network controlling the macro-mechanical behavior of coal. Improved understanding of the spatial characteristics of cleat networks is therefore important to the coal mining industry. Discrete fracture networks (DFNs) are increasingly used in engineering analyses to spatially model fractures at various scales. The reliability of coal DFNs largely depends on the confidence in the input cleat statistics. Estimates of these parameters can be made from image-based three-dimensional (3D) characterization of coal cleats using X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT). One key step in this process, after cleat extraction, is the separation of individual cleats, without which the cleats are a connected network and statistics for different cleat sets cannot be measured. In this paper, a feature extraction-based image processing method is introduced to identify and separate distinct cleat groups from 3D X-ray μCT images. Kernels (filters) representing explicit cleat features of coal are built and cleat separation is successfully achieved by convolutional operations on 3D coal images. The new method is applied to a coal specimen with 80 mm in diameter and 100 mm in length acquired from an Anglo American Steelmaking Coal mine in the Bowen Basin, Queensland, Australia. It is demonstrated that the new method produces reliable cleat separation capable of defining individual cleats and preserving 3D topology after separation. Bedding-parallel fractures are also identified and separated, which has historically been challenging to delineate and rarely reported. A variety of cleat/fracture statistics is measured which not only can quantitatively characterize the cleat/fracture system but also can be used for DFN modeling. Finally, variability and heterogeneity with respect to the core axis are investigated. Significant heterogeneity is observed and suggests that the representative elementary volume (REV) of the cleat groups for engineering purposes may be a complex problem requiring careful consideration.
[...]Read more. -
Evaluation of slope stability through rock mass classification and kinematic analysis of some major slopes along NH-1A from Ramban to Banihal, North Western Himalayas
Amit Jaiswal, A.K. Verma, T.N. Singh
2024, 16(1): 167-182. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.021
Abstract: The network of Himalayan roadways and highways connects some remote regions of valleys or hill slopes, which is vital for India's socio-economic growth. Due to natural and artificial factors, frequency of slope instabilities along the networks has been increasing over last few decades. Assessment of stability of natural and artificial slopes due to construction of these connecting road networks is significant in safeShow FiguresThe network of Himalayan roadways and highways connects some remote regions of valleys or hill slopes, which is vital for India's socio-economic growth. Due to natural and artificial factors, frequency of slope instabilities along the networks has been increasing over last few decades. Assessment of stability of natural and artificial slopes due to construction of these connecting road networks is significant in safely executing these roads throughout the year. Several rock mass classification methods are generally used to assess the strength and deformability of rock mass. This study assesses slope stability along the NH-1A of Ramban district of North Western Himalayas. Various structurally and non-structurally controlled rock mass classification systems have been applied to assess the stability conditions of 14 slopes. For evaluating the stability of these slopes, kinematic analysis was performed along with geological strength index (GSI), rock mass rating (RMR), continuous slope mass rating (CoSMR), slope mass rating (SMR), and Q-slope in the present study. The SMR gives three slopes as completely unstable while CoSMR suggests four slopes as completely unstable. The stability of all slopes was also analyzed using a design chart under dynamic and static conditions by slope stability rating (SSR) for the factor of safety (FoS) of 1.2 and 1 respectively. Q-slope with probability of failure (PoF) 1% gives two slopes as stable slopes. Stable slope angle has been determined based on the Q-slope safe angle equation and SSR design chart based on the FoS. The value ranges given by different empirical classifications were RMR (37–74), GSI (27.3–58.5), SMR (11–59), and CoSMR (3.39–74.56). Good relationship was found among RMR & SSR and RMR & GSI with correlation coefficient (R2) value of 0.815 and 0.6866, respectively. Lastly, a comparative stability of all these slopes based on the above classification has been performed to identify the most critical slope along this road.
[...]Read more. -
Effects of cement-enhanced soil on the ultimate lateral resistance of composite pile in clayey soil
Zhijun Yang, Kexin Chen, Xudong Fu, Zhiyan Zou
2024, 16(1): 183-191. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.010
Abstract: The composite pile consisting of core-pile and surrounding cement-enhanced soil is a promising pile foundation in recent years. However, how and to what extent the cement-enhanced soil influences the ultimate lateral resistance has not been fully investigated. In this paper, the ultimate lateral resistance of the composite pile was studied by finite element limit analysis (FELA) and theoretical upper-bound analysis.Show FiguresThe composite pile consisting of core-pile and surrounding cement-enhanced soil is a promising pile foundation in recent years. However, how and to what extent the cement-enhanced soil influences the ultimate lateral resistance has not been fully investigated. In this paper, the ultimate lateral resistance of the composite pile was studied by finite element limit analysis (FELA) and theoretical upper-bound analysis. The results of FELA and theoretical analysis revealed three failure modes of laterally loaded composite piles. The effects of the enhanced soil thickness, strength, and pile-enhanced soil interface characteristics on the ultimate lateral resistance were studied. The results show that increasing the enhanced soil thickness leads to a significant improvement on ultimate lateral resistance factor (NP), and there is a critical thickness beyond which the thickness no longer affects the NP. Increasing the enhanced soil strength induced 6.2%–232.6% increase of NP. However, no noticeable impact was detected when the enhanced soil strength was eight times higher than that of the natural soil. The maximum increment of NP is only 30.5% caused by the increase of interface adhesion factor (α). An empirical model was developed to calculate the NP of the composite pile, and the results show excellent agreement with the analytical results.
[...]Read more. -
Prediction of subsurface settlement induced by shield tunnelling in sandy cobble stratum
Fan Wang, Xiuli Du, Pengfei Li
2024, 16(1): 192-212. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.08.001
Abstract: This study focuses on the analytical prediction of subsurface settlement induced by shield tunnelling in sandy cobble stratum considering the volumetric deformation modes of the soil above the tunnel crown. A series of numerical analyses is performed to examine the effects of cover depth ratio (C/D), tunnel volume loss rate (ηt) and volumetric block proportion (VBP) on the characteristics of subsurface settlementShow FiguresThis study focuses on the analytical prediction of subsurface settlement induced by shield tunnelling in sandy cobble stratum considering the volumetric deformation modes of the soil above the tunnel crown. A series of numerical analyses is performed to examine the effects of cover depth ratio (C/D), tunnel volume loss rate (ηt) and volumetric block proportion (VBP) on the characteristics of subsurface settlement trough and soil volume loss. Considering the ground loss variation with depth, three modes are deduced from the volumetric deformation responses of the soil above the tunnel crown. Then, analytical solutions to predict subsurface settlement for each mode are presented using stochastic medium theory. The influences of C/D, ηt and VBP on the key parameters (i.e. B and N) in the analytical expressions are discussed to determine the fitting formulae of B and N. Finally, the proposed analytical solutions are validated by the comparisons with the results of model test and numerical simulation. Results show that the fitting formulae provide a convenient and reliable way to evaluate the key parameters. Besides, the analytical solutions are reasonable and available in predicting the subsurface settlement induced by shield tunnelling in sandy cobble stratum.
[...]Read more. -
Uncertainties of landslide susceptibility prediction: Influences of random errors in landslide conditioning factors and errors reduction by low pass filter method
Faming Huang, Zuokui Teng, Chi Yao, Shui-Hua Jiang, Filippo Catani, Wei Chen, Jinsong Huang
2024, 16(1): 213-230. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.11.001
Abstract: In the existing landslide susceptibility prediction (LSP) models, the influences of random errors in landslide conditioning factors on LSP are not considered, instead the original conditioning factors are directly taken as the model inputs, which brings uncertainties to LSP results. This study aims to reveal the influence rules of the different proportional random errors in conditioning factors on the LSP uncertaintiShow FiguresIn the existing landslide susceptibility prediction (LSP) models, the influences of random errors in landslide conditioning factors on LSP are not considered, instead the original conditioning factors are directly taken as the model inputs, which brings uncertainties to LSP results. This study aims to reveal the influence rules of the different proportional random errors in conditioning factors on the LSP uncertainties, and further explore a method which can effectively reduce the random errors in conditioning factors. The original conditioning factors are firstly used to construct original factors-based LSP models, and then different random errors of 5%, 10%, 15% and 20% are added to these original factors for constructing relevant errors-based LSP models. Secondly, low-pass filter-based LSP models are constructed by eliminating the random errors using low-pass filter method. Thirdly, the Ruijin County of China with 370 landslides and 16 conditioning factors are used as study case. Three typical machine learning models, i.e. multilayer perceptron (MLP), support vector machine (SVM) and random forest (RF), are selected as LSP models. Finally, the LSP uncertainties are discussed and results show that: (1) The low-pass filter can effectively reduce the random errors in conditioning factors to decrease the LSP uncertainties. (2) With the proportions of random errors increasing from 5% to 20%, the LSP uncertainty increases continuously. (3) The original factors-based models are feasible for LSP in the absence of more accurate conditioning factors. (4) The influence degrees of two uncertainty issues, machine learning models and different proportions of random errors, on the LSP modeling are large and basically the same. (5) The Shapley values effectively explain the internal mechanism of machine learning model predicting landslide susceptibility. In conclusion, greater proportion of random errors in conditioning factors results in higher LSP uncertainty, and low-pass filter can effectively reduce these random errors.
[...]Read more. -
Monitoring shear deformation of sliding zone via fiber Bragg grating and particle image velocimetry
Deyang Wang, Honghu Zhu, Guyu Zhou, Wenzhao Yu, Baojun Wang, Wanhuan Zhou
2024, 16(1): 231-241. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.007
Abstract: Monitoring shear deformation of sliding zones is of great significance for understanding the landslide evolution mechanism, in which fiber optic strain sensing has shown great potential. However, the correlation between strain measurements of quasi-distributed fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensing arrays and shear displacements of surrounding soil remains elusive. In this study, a direct shear model test was conducted toShow FiguresMonitoring shear deformation of sliding zones is of great significance for understanding the landslide evolution mechanism, in which fiber optic strain sensing has shown great potential. However, the correlation between strain measurements of quasi-distributed fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensing arrays and shear displacements of surrounding soil remains elusive. In this study, a direct shear model test was conducted to simulate the shear deformation of sliding zones, in which the soil internal deformation was captured using FBG strain sensors and the soil surface deformation was measured by particle image velocimetry (PIV). The test results show that there were two main slip surfaces and two secondary ones, developing a spindle-shaped shear band in the soil. The formation of the shear band was successfully captured by FBG sensors. A sinusoidal model was proposed to describe the fiber optic cable deformation behavior. On this basis, the shear displacements and shear band widths were calculated by using strain measurements. This work provides important insight into the deduction of soil shear deformation using soil-embedded FBG strain sensors.
[...]Read more. -
Extended wet sieving method for determination of complete particle size distribution of general soils
Shengnan Ma, Yi Song, Jiawei Liu, Xingyu Kang, Zhongqi Quentin Yue
2024, 16(1): 242-257. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.03.006
Abstract: The traditional standard wet sieving method uses steel sieves with aperture ≥0.063 mm and can only determine the particle size distribution (PSD) of gravel and sand in general soil. This paper extends the traditional method and presents an extended wet sieving method. The extended method uses both the steel sieves and the nylon filter cloth sieves. The apertures of the cloth sieves are smaller than 0.063 mm and eqShow FiguresThe traditional standard wet sieving method uses steel sieves with aperture ≥0.063 mm and can only determine the particle size distribution (PSD) of gravel and sand in general soil. This paper extends the traditional method and presents an extended wet sieving method. The extended method uses both the steel sieves and the nylon filter cloth sieves. The apertures of the cloth sieves are smaller than 0.063 mm and equal 0.048 mm, 0.038 mm, 0.014 mm, 0.012 mm, 0.0063 mm, 0.004 mm, 0.003 mm, 0.002 mm, and 0.001 mm, respectively. The extended method uses five steps to separate the general soil into many material sub-groups of gravel, sand, silt and clay with known particle size ranges. The complete PSD of the general soil is then calculated from the dry masses of the individual material sub-groups. The extended method is demonstrated with a general soil of completely decomposed granite (CDG) in Hong Kong, China. The silt and clay materials with different particle size ranges are further examined, checked and verified using stereomicroscopic observation, physical and chemical property tests. The results further confirm the correctness of the extended wet sieving method.
[...]Read more. -
Analytical evaluation of steady-state solute distribution in through-diffusion and membrane behavior test under non-perfectly flushing boundary conditions
Guannian Chen, Yuchao Li, Kristin M. Sample-Lord, Shan Tong
2024, 16(1): 258-267. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.010
Abstract: The through-diffusion and membrane behavior testing procedure using a closed-system apparatus has been widely used for concurrent measurement of diffusion and membrane efficiency coefficients of low-permeability clay-based barrier materials. However, the common assumption of perfectly flushing conditions at the specimen boundaries could induce errors in analyses of the diffusion coefficients and membrane efficienciesShow FiguresThe through-diffusion and membrane behavior testing procedure using a closed-system apparatus has been widely used for concurrent measurement of diffusion and membrane efficiency coefficients of low-permeability clay-based barrier materials. However, the common assumption of perfectly flushing conditions at the specimen boundaries could induce errors in analyses of the diffusion coefficients and membrane efficiencies. In this study, an innovative pseudo three-dimensional (3D) analytical method was proposed to evaluate solute distribution along the boundary surfaces of the soil-porous disks system, considering the non-perfectly flushing conditions. The results were consistent with numerical models under two scenarios considering different inflow/outflow positions. The proposed model has been demonstrated to be an accurate and reliable method to estimate solute distributions along the boundaries. The calculated membrane efficiency coefficient and diffusion coefficient based on the proposed analytical method are more accurate, resulting in up to 50% less relative error than the traditional approach that adopts the arithmetic mean value of the influent and effluent concentrations. The retardation factor of the clay specimen also can be calculated with a revised cumulative mass approach. Finally, the simulated transient solute transport matched with experimental data from a multi-stage through-diffusion and membrane behavior test, validating the accuracy of the proposed method.
[...]Read more. -
Spatiotemporal variations of sand hydraulic conductivity by microbial application methods
Viroon Kamchoom, Thiti Khattiwong, Treesukon Treebupachatsakul, Suraparb Keawsawasvong, Anthony Kwan Leung
2024, 16(1): 268-278. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.04.024
Abstract: The spatiotemporal distributions of microbes in soil by different methods could affect the efficacy of the microbes to reduce the soil hydraulic conductivity. In this study, the specimens of bio-mediated sands were prepared using three different methods, i.e. injecting, mixing, and pouring a given microbial solution onto compacted sand specimens. The hydraulic conductivity was measured by constant-head tests, while aShow FiguresThe spatiotemporal distributions of microbes in soil by different methods could affect the efficacy of the microbes to reduce the soil hydraulic conductivity. In this study, the specimens of bio-mediated sands were prepared using three different methods, i.e. injecting, mixing, and pouring a given microbial solution onto compacted sand specimens. The hydraulic conductivity was measured by constant-head tests, while any soil microstructural changes due to addition of the microbes were observed by scanning electron microscope (SEM) and mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) tests. The amount of dextran concentration produced by microbes in each type of specimen was quantified by a refractometer. Results show that dextran production increased exponentially after 5–7 d of microbial settling with the supply of culture medium. The injection and mixing methods resulted in a similar amount and uniform distribution of dextran in the specimens. The pouring method, however, produced a nonuniform distribution, with a higher concentration near the specimen surface. As the supply of culture medium discontinued, the dextran content near the surface produced by the pouring method decreased dramatically due to high competition for nutrients with foreign colonies. Average dextran concentration was negatively and correlated with hydraulic conductivity of bio-mediated soils exponentially, due to the clogging of large soil pores by dextran. The hydraulic conductivity of the injection and mixing cases did not change significantly when the supply of culture medium was absent.
[...]Read more. -
Modelling smear effect of vertical drains using a diameter reduction method
Zhichao Shen, Siau Chen Chian, Siew Ann Tan, Chun Fai Leung
2024, 16(1): 279-290. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.06.021
Abstract: Vertical drains are used to accelerate consolidation of clays in ground improvement projects. Smear zones exist around these drains, where permeability is reduced due to soil disturbance caused by the installation process. Hansbo solution is widely used in practice to consider the effects of drain discharge capacity and smear on the consolidation process. In this study, a computationally efficient diameter reductionShow FiguresVertical drains are used to accelerate consolidation of clays in ground improvement projects. Smear zones exist around these drains, where permeability is reduced due to soil disturbance caused by the installation process. Hansbo solution is widely used in practice to consider the effects of drain discharge capacity and smear on the consolidation process. In this study, a computationally efficient diameter reduction method (DRM) obtained from the Hansbo solution is proposed to consider the smear effect without the need to model the smear zone physically. Validated by analytical and numerical results, a diameter reduction factor is analytically derived to reduce the diameter of the drain, while achieving similar solutions of pore pressure dissipation profile as the classical full model of the smear zone and drain. With the DRM, the excess pore pressure u obtained from the reduced drain in the original undisturbed soil zone is accurate enough for practical applications in numerical models. Such performance of DRM is independent of soil material property. Results also show equally accurate performance of DRM under conditions of multi-layered soils and coupled radial-vertical groundwater flow.
[...]Read more. -
Effect of drying-wetting cycles on pore characteristics and mechanical properties of enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation-reinforced sea sand
Ming Huang, Kai Xu, Zijian Liu, Chaoshui Xu, Mingjuan Cui
2024, 16(1): 291-302. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.12.032
Abstract: Enzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) is an emanating, eco-friendly and potentially sound technique that has presented promise in various geotechnical applications. However, the durability and microscopic characteristics of EICP-treated specimens against the impact of drying-wetting (D-W) cycles is under-explored yet. This study investigates the evolution of mechanical behavior and pore characteristics of EICShow FiguresEnzyme-induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) is an emanating, eco-friendly and potentially sound technique that has presented promise in various geotechnical applications. However, the durability and microscopic characteristics of EICP-treated specimens against the impact of drying-wetting (D-W) cycles is under-explored yet. This study investigates the evolution of mechanical behavior and pore characteristics of EICP-treated sea sand subjected to D-W cycles. The uniaxial compressive strength (UCS) tests, synchrotron radiation micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction of CT images were performed to study the multiscale evolution characteristics of EICP-reinforced sea sand under the effect of D-W cycles. The potential correlations between microstructure characteristics and macro-mechanical property deterioration were investigated using gray relational analysis (GRA). Results showed that the UCS of EICP-treated specimens decreases by 63.7% after 15 D-W cycles. The proportion of mesopores gradually decreases whereas the proportion of macropores increases due to the exfoliated calcium carbonate with increasing number of D-W cycles. The microstructure in EICP-reinforced sea sand was gradually disintegrated, resulting in increasing pore size and development of pore shape from ellipsoidal to columnar and branched. The gray relational degree suggested that the weight loss rate and UCS deterioration were attributed to the development of branched pores with a size of 100–1000 μm under the action of D-W cycles. Overall, the results in this study provide a useful guidancee for the long-term stability and evolution characteristics of EICP-reinforced sea sand under D-W weathering conditions.
[...]Read more. -
Modelling the viscoplastic behaviour of Callovo-Oxfordian claystone with consideration of damage effect
Hao Wang, Yu-Jun Cui, Minh Ngoc Vu, Jean Talandier
2024, 16(1): 303-316. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.09.001
Abstract: In order to evaluate the performance of deep geological disposal of radioactive waste, an underground research laboratory (URL) was constructed by Andra in the Callovo-Oxfordian (COx) claystone formation at the Meuse/Haute-Marne (MHM). The construction of URL induced the excavation damage of host formations, and the ventilation in the galleries desaturated the host formation close to the gallery wall. Moreover, it isShow FiguresIn order to evaluate the performance of deep geological disposal of radioactive waste, an underground research laboratory (URL) was constructed by Andra in the Callovo-Oxfordian (COx) claystone formation at the Meuse/Haute-Marne (MHM). The construction of URL induced the excavation damage of host formations, and the ventilation in the galleries desaturated the host formation close to the gallery wall. Moreover, it is expected that the mechanical behaviour of COx claystone is time-dependent. This study presents a constitutive model developed to describe the viscoplastic behaviour of unsaturated and damaged COx claystone. In this model, the unsaturation effect is considered by adopting the Bishop effective stress and the van Genuchten (VG) water retention model. In terms of the viscoplastic behaviour, the nonstationary flow surface (NSFS) theory for unsaturated soils is used with consideration of the coupled effects of strain rate and suction on the yield stress. A progressive hardening law is adopted. Meanwhile, a non-associated flow rule is used, which is similar to that in Barcelona basic model (BBM). In addition, to describe the damage effect induced by suction change and viscoplastic loading, a damage function is defined based on the crack volume proportion. This damage function contains two variables: unsaturated effective stress and viscoplastic volumetric strain, with the related parameters determined based on the mercury intrusion porosimetry (MIP) tests. For the model validation, different tests on COx claystone under different loading paths are simulated. Comparisons between experimental and simulated results indicated that the present model is able to well describe the viscoplastic behaviour of damaged COx claystone, including swelling/shrinkage, triaxial extension and compression, and triaxial creep.
[...]Read more. -
Prediction of high-embankment settlement combining joint denoising technique and enhanced GWO-ν-SVR method
Qi Zhang, Qian Su, Zongyu Zhang, Zhixing Deng, De Chen
2024, 16(1): 317-332. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.06.018
Abstract: Reliable long-term settlement prediction of a high embankment relates to mountain infrastructure safety. This study developed a novel hybrid model (NHM) that combines a joint denoising technique with an enhanced gray wolf optimizer (EGWO)-ν-support vector regression (ν-SVR) method. High-embankment field measurements were preprocessed using the joint denoising technique, which includes complete ensemble empiricaShow FiguresReliable long-term settlement prediction of a high embankment relates to mountain infrastructure safety. This study developed a novel hybrid model (NHM) that combines a joint denoising technique with an enhanced gray wolf optimizer (EGWO)-ν-support vector regression (ν-SVR) method. High-embankment field measurements were preprocessed using the joint denoising technique, which includes complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition, singular value decomposition, and wavelet packet transform. Furthermore, high-embankment settlements were predicted using the EGWO-ν-SVR method. In this method, the standard gray wolf optimizer (GWO) was improved to obtain the EGWO to better tune the ν-SVR model hyperparameters. The proposed NHM was then tested in two case studies. Finally, the influences of the data division ratio and kernel function on the EGWO-ν-SVR forecasting performance and prediction efficiency were investigated. The results indicate that the NHM suppresses noise and restores details in high-embankment field measurements. Simultaneously, the NHM outperforms other alternative prediction methods in prediction accuracy and robustness. This demonstrates that the proposed NHM is effective in predicting high-embankment settlements with noisy field measurements. Moreover, the appropriate data division ratio and kernel function for EGWO-ν-SVR are 7:3 and radial basis function, respectively.
[...]Read more. -
Fiber optic monitoring of an anti-slide pile in a retrogressive landslide
Lei Zhang, Honghu Zhu, Heming Han, Bin Shi
2024, 16(1): 333-343. doi:10.1016/j.jrmge.2023.02.011
Abstract: Anti-slide piles are one of the most important reinforcement structures against landslides, and evaluating the working conditions is of great significance for landslide mitigation. The widely adopted analytical methods of pile internal forces include cantilever beam method and elastic foundation beam method. However, due to many assumptions involved in calculation, the analytical models cannot be fully applicable toShow FiguresAnti-slide piles are one of the most important reinforcement structures against landslides, and evaluating the working conditions is of great significance for landslide mitigation. The widely adopted analytical methods of pile internal forces include cantilever beam method and elastic foundation beam method. However, due to many assumptions involved in calculation, the analytical models cannot be fully applicable to complex site situations, e.g. landslides with multi-sliding surfaces and pile-soil interface separation as discussed herein. In view of this, the combination of distributed fiber optic sensing (DFOS) and strain-internal force conversion methods was proposed to evaluate the working conditions of an anti-sliding pile in a typical retrogressive landslide in the Three Gorges reservoir area, China. Brillouin optical time domain reflectometry (BOTDR) was utilized to monitor the strain distribution along the pile. Next, by analyzing the relative deformation between the pile and its adjacent inclinometer, the pile-soil interface separation was profiled. Finally, the internal forces of the anti-slide pile were derived based on the strain-internal force conversion method. According to the ratio of calculated internal forces to the design values, the working conditions of the anti-slide pile could be evaluated. The results demonstrated that the proposed method could reveal the deformation pattern of the anti-slide pile system, and can quantitatively evaluate its working conditions.
[...]Read more. -
Reviewer acknowledgements
Editorial Office of JRMGE
2024, 16(1): 344-344. doi:10.1016/S1674-7755(23)00354-2.
Abstract: [...]Read more.